Tutorial
This tutorial will guide you through all the steps needed to (i) add new data sources to WARCProcessor, (ii) understand all kind of datasources and their parameters, (iii) configure the properties of output corpora and finally, (iv) build your corpora.
Contents
1 Creating WARCProcessor Datasources
In order to carry out empirical experiments to solve web-spam problem, researchers should compile different collections of spam and ham web sites. WARCProcessor compiles information sources (datasources) to build required datasets for research. A datasource is a mechanism that provide classified websites to be included into an output dataset.
WARCProcessor currently supports 5 kinds of datasources including: (i) CSVDS, (ii) ArffDS, (iii) FileDS, (iv) WarcDS and (v) CorpusDS.
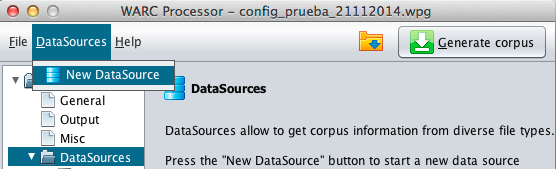
Every datasources can be easily created using the "New" option from "Datasource" menu.
Press the "New" button on the toolbar.

Automatically WARCProcessor shows in its right side the assistant to
guide throw the process of creating a new Data Source.
In the assistant pannel, you should click the button "New Datasource"
The first step of the assistant prompts for the following Data Source information: (i) Name (useful to identificate the datasource), (2) path to Data Source files (where input files are located) and, finally (iii) Data Source type (please see subsections).
After filling the information, user should use the button "Continue" to advance to next window.
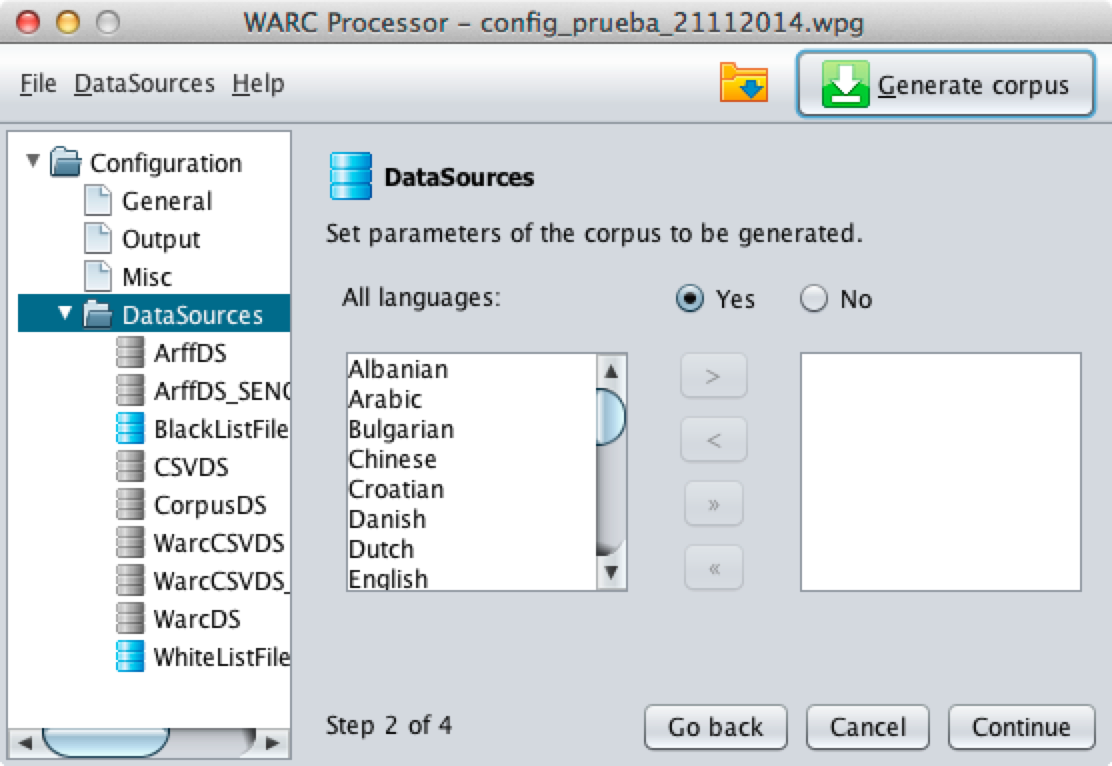
The second parameter allows user to discard from Data Sources information sites that are not write in a specified set of languages.
If a language source filtering is not required for experimentation
purposes you can keep de default value for the property "All languages".
However, if you want to filter languages, you can select "No" for this
property and select required languages using lists shown below.
When language configuration issues get defined "Continue" button will
present the specific datasource configuration section.
The specific configuration section compiles detailed properties of the
dataset. You should note that "Parameters" section is specific for each
kind of dataset (please see subsections to discover how to configure
each kind of dataset).
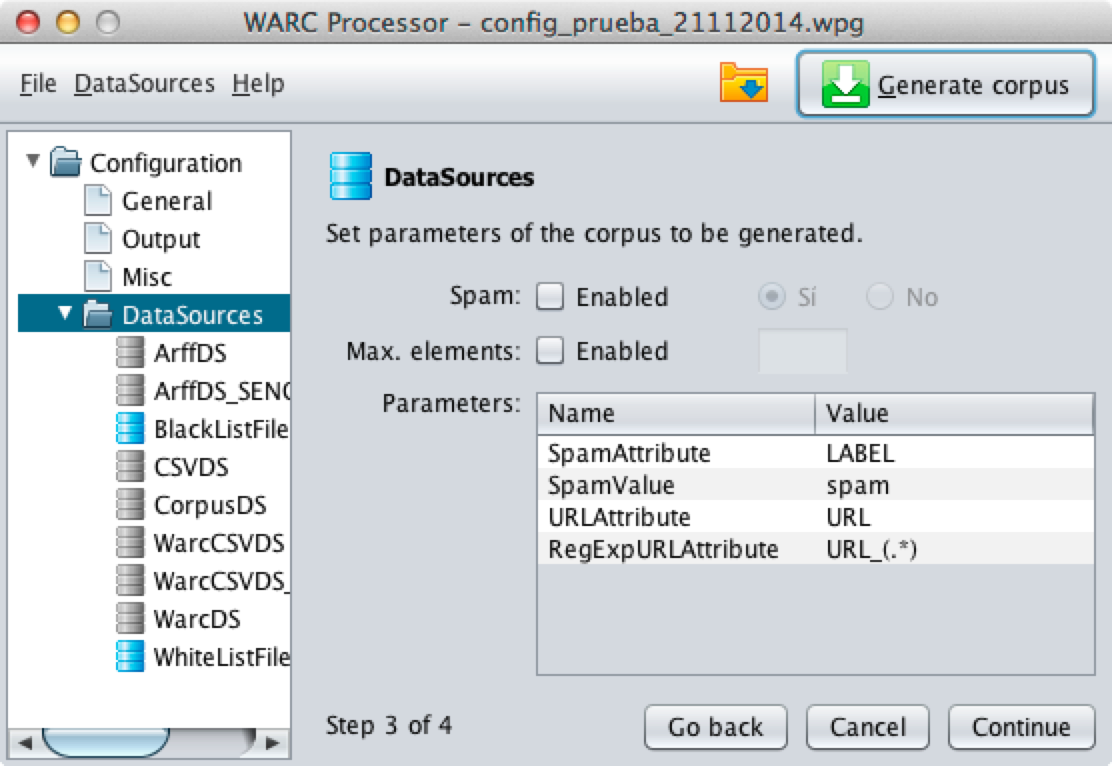
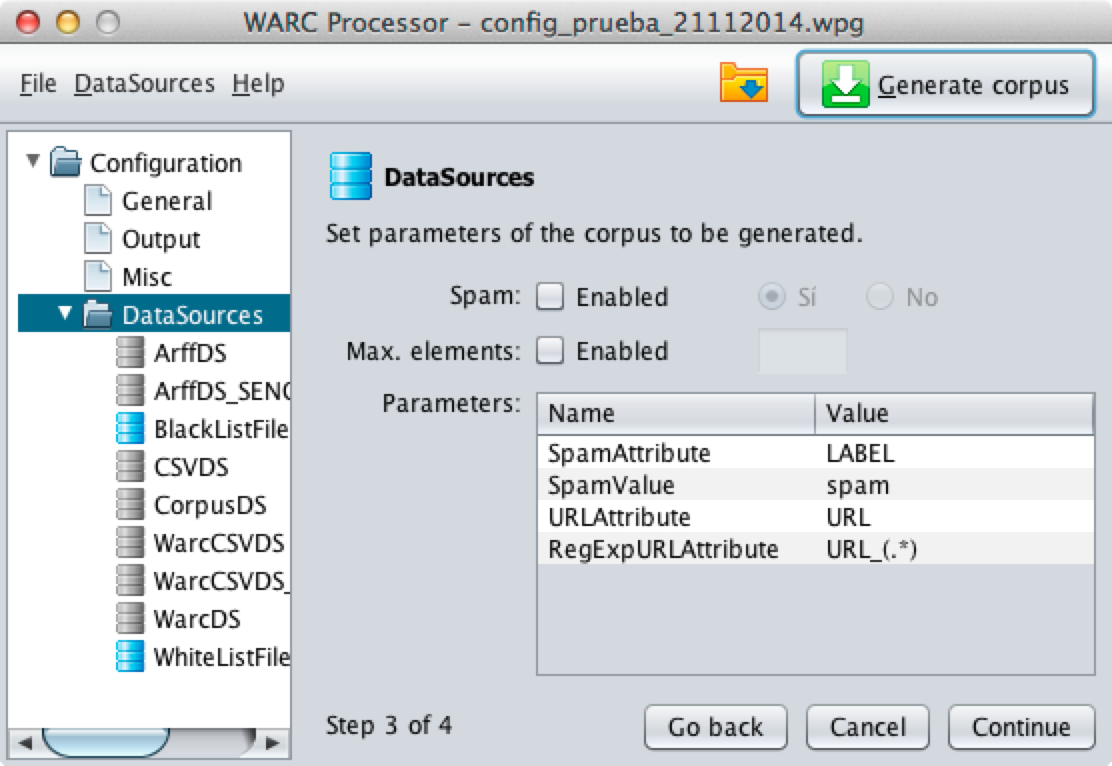
The check "Spam" should be enabled if all instances (sites) included in
the Data Source belongs to the same class (spam|ham). If yes, user
must select if message is spam or not. This feature should be used
only when the Data Set does not include information about the class of
each website and all websites belongs to the same class.
"Max Elements" option allows to limit the maximum number of elements
(websites) that can be extracted from the current Data Source when
composing each corpora.
After configuring properly these options and the "Parameters" section
(specific for each kind of dataset), user should use "Continue" button
to advance to the confirmation section.
The last screen of the assistant show all values compiled during its steps to confirm the information included in the dataset. If the information is right, user can press the button "Finalize" to finish the assistant and create the dataset. Otherwise, user can step backward using the button "Go back" to fix errors in previous steps.
Next subsections presents the different kinds of Data Sources including their file/directory structure and the parameters to be configured in the third step of the assistant.
1.1 CSVDS and ArffDS datasources
These kind of datasources are based on the usage of CSV (using the format defined in RFC 4180) and ARFF files (defined by Weka creators in "http://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/arff.html). These kind of files support the usage of information structured in columns. Thus, each row contains information relative to a website and each column compile the values for a certain attribute. To be usable these kind of datasources should include a column indicating the URL of the website and the classification of websites should be posible (using a column included in the target files or including only sites belonging the same class). These kinds of datasources require the downloading of the target websites.
These kinds of datasources are composed of one or more files with the
same structure included in a directory. The directory containing CSV
and ARFF files (respectively) is the path that should be specified in
the first step of the dataset definition. Moreover, the next table
represents the parameters that can be defined by each dataset and
the possible values for them:
CSV
| Attribute | Description | Posible values |
|---|---|---|
| FieldSeparator | Character used as field separator (CSV format) | A character (common values are ; or ,) |
| HeaderRowPresent | Indicates if the first file contain the name of the attribute or not | true or false |
| SpamValue | Identifies the column that contains the class of the target site | Name of the column (if HeaderRowPresent=true) or number of the column |
| SpamValue | Value of the attribute specified by SpamValue when the site is spam | Literal with the value |
| URLAttribute | Identifies the column that contains the URL of the target site | Name of the column (if HeaderRowPresent=true) or number of the column |
| RegExpURLAttribute | Allows defining a RegularExpression to delete some text from URLAttribute (if required) | Regular expression where (.*) stands for the target URL |
ARFF
| Attribute | Description | Posible values |
|---|---|---|
| SpamValue | Identifies the column that contains the class of the target site | Name of the column |
| SpamValue | Value of the attribute specified by SpamValue when the site is spam | Literal with the value |
| URLAttribute | Identifies the column that contains the URL of the target site | Name of the column |
| RegExpURLAttribute | Allows defining a RegularExpression to delete some text from URLAttribute (if required) | Regular expression where (.*) stands for the target URL |
1.2 FileDS Datasources
A FileDS datasource uses one or more text files (TXT) to define datasources. These files usually uses .txt or .text file extensions. The datasource path should be a folder containing one or more .txt files where each URL is placed in a single line of the file with no adicional information. This kind of datasources require the downloading of the target websites.
A FileDS should be defined as a whitelist or a blacklist of URLs where URLs are separated by "\n" character. Thus, this kind of datasources should be used in conjunction with the "Spam" option defined in the third step of the assistant to manually determine if websites included in them are all spam or ham.
Finally, a FileDS datasource does not require adicional configuration parameters.
1.3 WarcDS Datasources
A WarcDS datasource is comprised by a directory containing one or more WARC files (.warc). As long as WARC files does not allow to include a classification attribute for each stored site, the class of the sites included in them should be manually indicated though using Spam configuration option in the third step of the assistant. To configure the datasource, the directory containing all WARC files should be specified as datasource path.
This kind of datasources should contain the attributes specified in the
next table:
| Attribute | Description | Posible values |
|---|---|---|
| WarcURLTag | Identifies the WARC entry attribute name that contains the URL of the target site | Name of a WARC entry attribute |
| RegExpURLAttribute | Allows defining a RegularExpression to delete some text from URLAttribute (if required) | Regular expression where (.*) stands for the target URL |
1.4 WarcCSVDS Datasources
WarcCSVDS combines a WARC datasource with a CSVDS datasource indicating the class of each website included in WARC files. Thus, this datasource combination solves the weaknesses of both combined datasources:
- A CSVDS datasource does not include a copy of the target sites. This information should be downloaded when required. As long as online information can change, we should be care about using this kind of sources (download as soon as possible and convert them on other kinds of datasources).
- A WarcDS does not provide the classification of each web site. Therefore all sites included in this kind of datasources should have the same class and the usage of manual classification option ("Spam" attribute included in the third step of assistant) is required.
Although WarcCSVDS datasources can contain multiple WARC files, the number of CSV files is limited to 1. A directory containing all WARC files and the CSV file should be specified as datasource path.
Finally, this kind of datasources should include the following parameters:
| Attribute | Description | Posible values |
|---|---|---|
| WarcURLTag | Identifies the WARC entry attribute name that contains the URL of the target site | Name of a WARC entry attribute |
| RegExpURLAttribute | Allows defining a RegularExpression to delete some text from URLAttribute (if required) in CSV and WARC files | Regular expression where (.*) stands for the target URL |
| FieldSeparator | Character used as field separator (CSV format) | A character (common values are ; or ,) |
| URLAttribute | Identifies the column that contains the URL of the target site | Name of the column (if HeaderRowPresent=true) or number of the column |
| SpamValue | Value of the attribute specified by SpamValue when the site is spam | Literal with the value |
| HeaderRowPresent | Indicates if the first file contain the name of the attribute or not | true or false |
| FileCSV | The relative path (regarding dataset) to CSV file | Relative path to CSV file |
1.5 CorpusDS Datasources
A CorpusDS datasource combines the usage of several WARC files included into one of two subfolders: (i) spam and (ii) ham. The name of ham and spam subfolders can be customized by user (_ham_ and _spam_ by default). Therefore the dataset path should be configured as a folder containing the spam and ham subfolders. Each WARC file can contain one or more sites belonging to the same class.
The parameters for this kind of corpus are the following ones:
| Attribute | Description | Posible values |
|---|---|---|
| WarcURLTag | Identifies the WARC entry attribute name that contains the URL of the target site | Name of a WARC entry attribute |
| RegExpURLAttribute | Allows defining a RegularExpression to delete some text from URLAttribute (if required) in CSV and WARC files | Regular expression where (.*) stands for the target URL |
| SpamDir | Indicates the name of the spam subfolder | The name of the spam subfolder (_spam_ by default) |
| HamDir | Indicates the name of the ham (legitimate) subfolder | The name of the ham subfolder (_ham_ by default) |
The output corpora generated by WARCProcessor have this format and each site is represented in a separate WARC file.
2 Configuring the output corpus
The main purpose of WARCProcessor is the automation of generating a corpus for web spam from a group of datasources. Previous section showed how to create and configure different kinds of datasources.
WARCProcessor allows the usage of different features to compose an
output corpus:
- Selection of input Datasources: Datasources can be easilly enabled or disabled with the purpose of include/exclude them in the output corpus generation.
- Language filtering: Each datasource includes a language filter that can be easily enabled to avoid the inclusion of sites in certain languages in the output corpus.
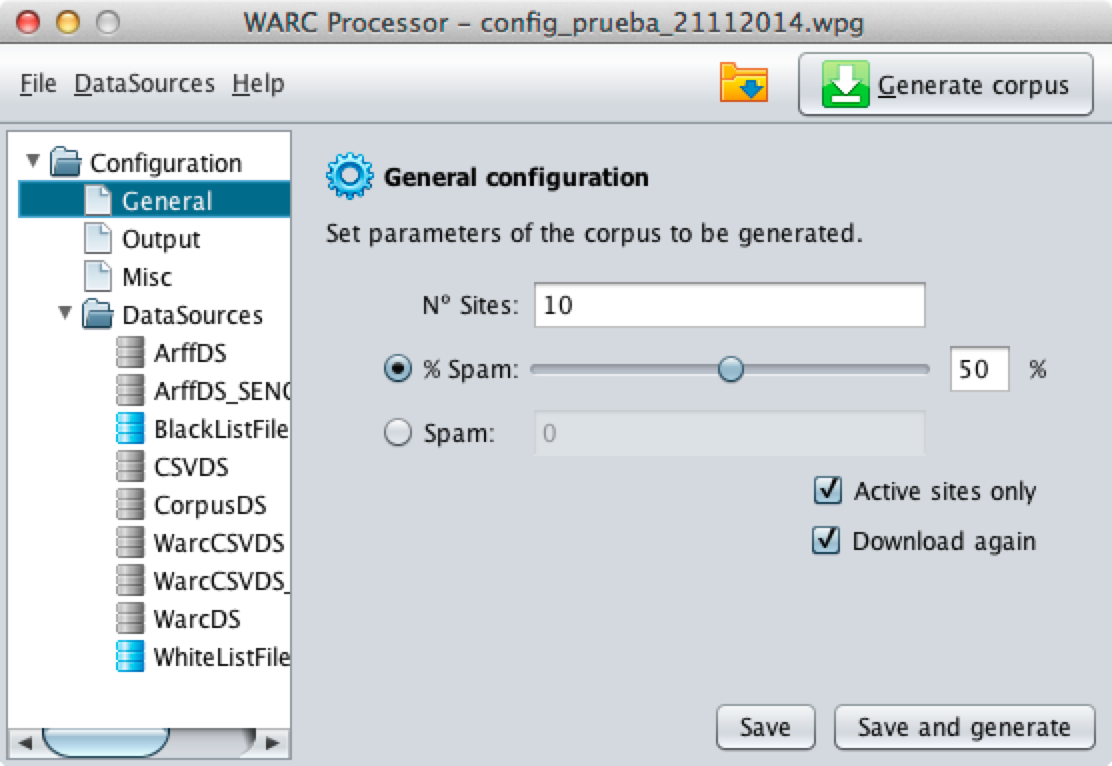
- Limit the number of sites: WARCProcessor general configuration requires the number of sites to be included in a output corpus.
- Number of spam sites: General configuration include the possibility of establish the percentage of spam messages in the whole output corpus or the specific number of spam sites.
- Site deep scanning: WARCProcessor allows establishing the deep of downloading of sites that should be downloaded for corpus creation.
2.1 Enabling/Disabling datasources
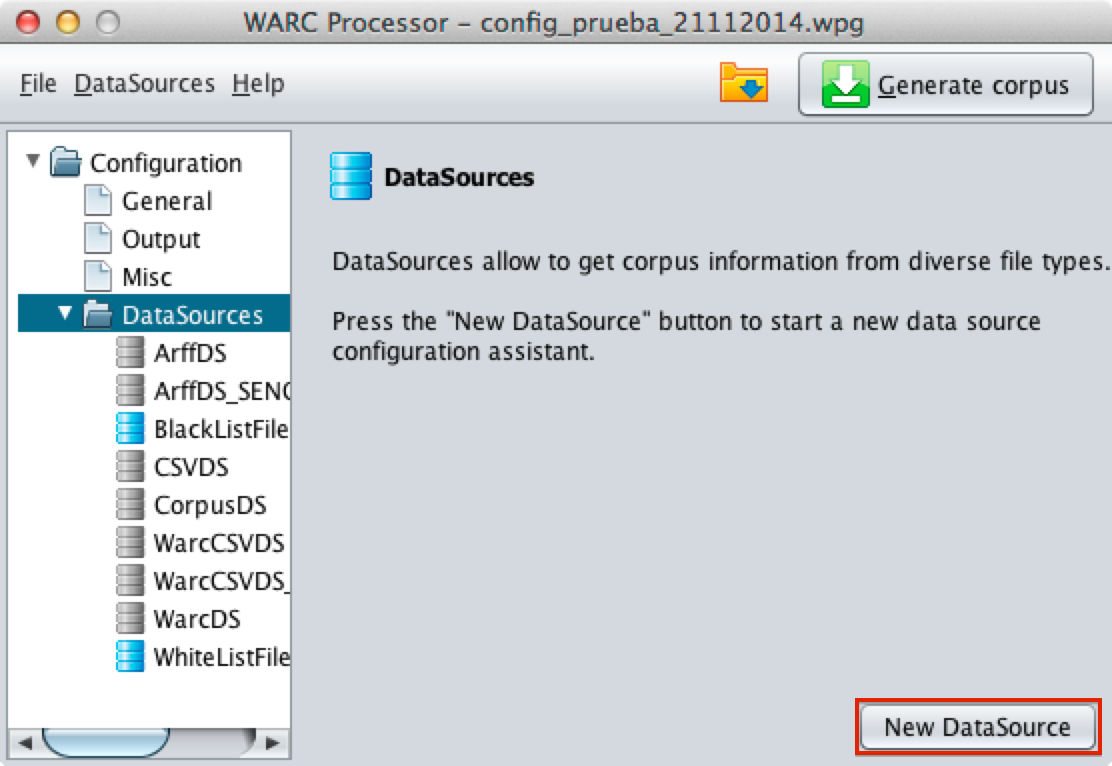
Datasources can be easily enabled or disabled for the purposes of generating output datasets. As seen in the tree at the left side of WARCProcessor main window, a "Datasources" folder can be found. User should expand the folder to see datasets (if folder is collapsed) by clicking in the folder icon.
As seen, in the last figure, datasources enabled has a blue icon while disabled ones are grey. Once user select a specific datasource, it can be easily disabled by unchecking the box "Enabled". Moreover, checking again this box, the datasource gets enabled again.
2.2 Filtering languages
As above shown, each datasource has an associate language filter.
In order to reedit a datasource and change language filter, we should select the dataset from the tree (left side of WARCProcessor) and clic on the "Modify" button.
2.3 Configuring output dataset
In order to configure the output dataset, WARCProcessor incorporates three configuration panels that can be easily shown using left side tree. These panels are: (i) General, (ii) Output and (iii) Misc.
General configuration allows stablishing the number of sites to include in the output corpus as well as the percentage of spam sites or a fixed number of spam instances.
Moreover, General configuration options allow to discard sites that are currently not available and even force the downloading of the target sites.
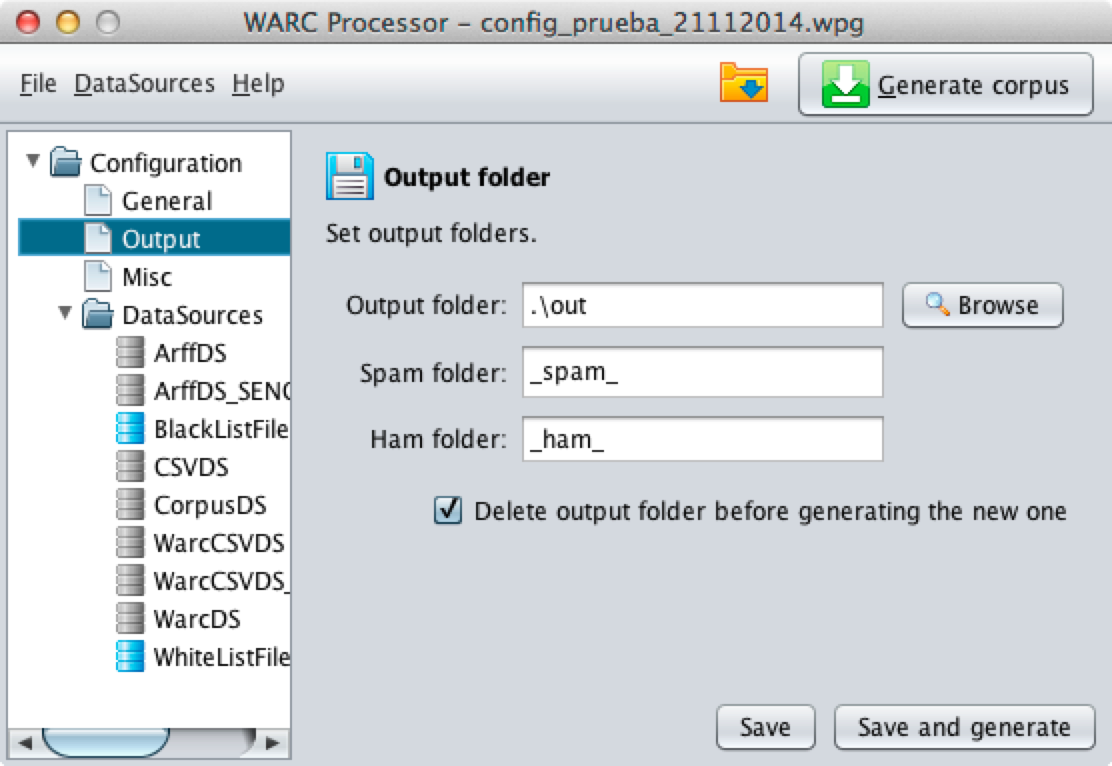
The Output configuration allows user selecting a folder to generate the output corpus and the name for spam and ham subfolders.
Moreover, as shown, Output configuration allows to indicate WARCProcessor to remove all contents of output folder before generating the new corpus. Use this option carefully.
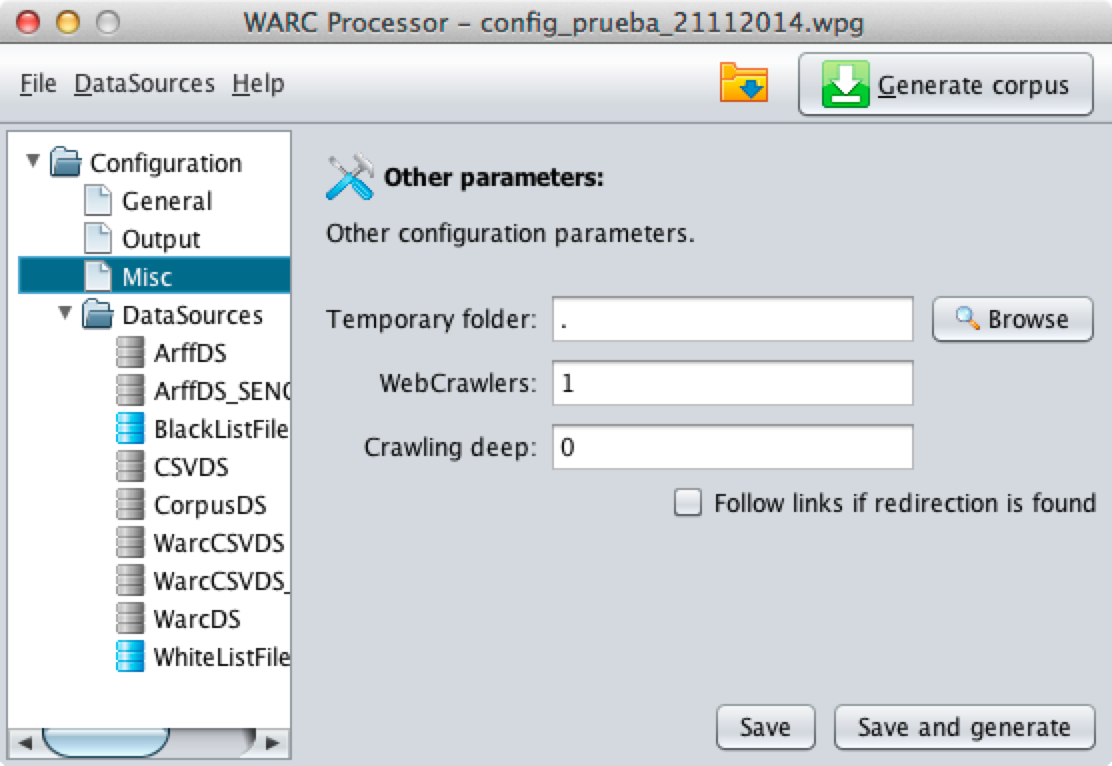
Finally, Misc configuration contains internal parameters for the operation of WARCProcessor app. The parameters include a temporary folder, the number of threads for the web-crawler, the deep of site scanning (0 infinite) and if a redirection should be followed when found in the main site.
3 Batch processing
Although an output corpus can be generated using the button "Generate Corpus" located at the right top of the main window, WARCProcessor allows a batch corpus generation method. To this end, user uses the GUI (Graphical User Interface) to generate and save a configuration file (File -> Save as). Then, WARCGenerator can be invoked with the flag --no-gui to work in batch mode.