Getting Started
Table of contents
2. Inside an in silico project
2.3. Generating NEXUS and tree files
3. Inside a m/z profile project
3.1 M/z profile project status
Uploading your projects
First things first. P4P allows the creation of two types of projects: in silico or m/z profile projects. In silico projects are based on genome data (“.faa” files) and entail the generation of the corresponding peptidomes by computational methods. P4P can also accept as input experimental mass-to-charge lists originated from mass spectrometers.
New in silico project
In in silico projects there are five fields to fill:
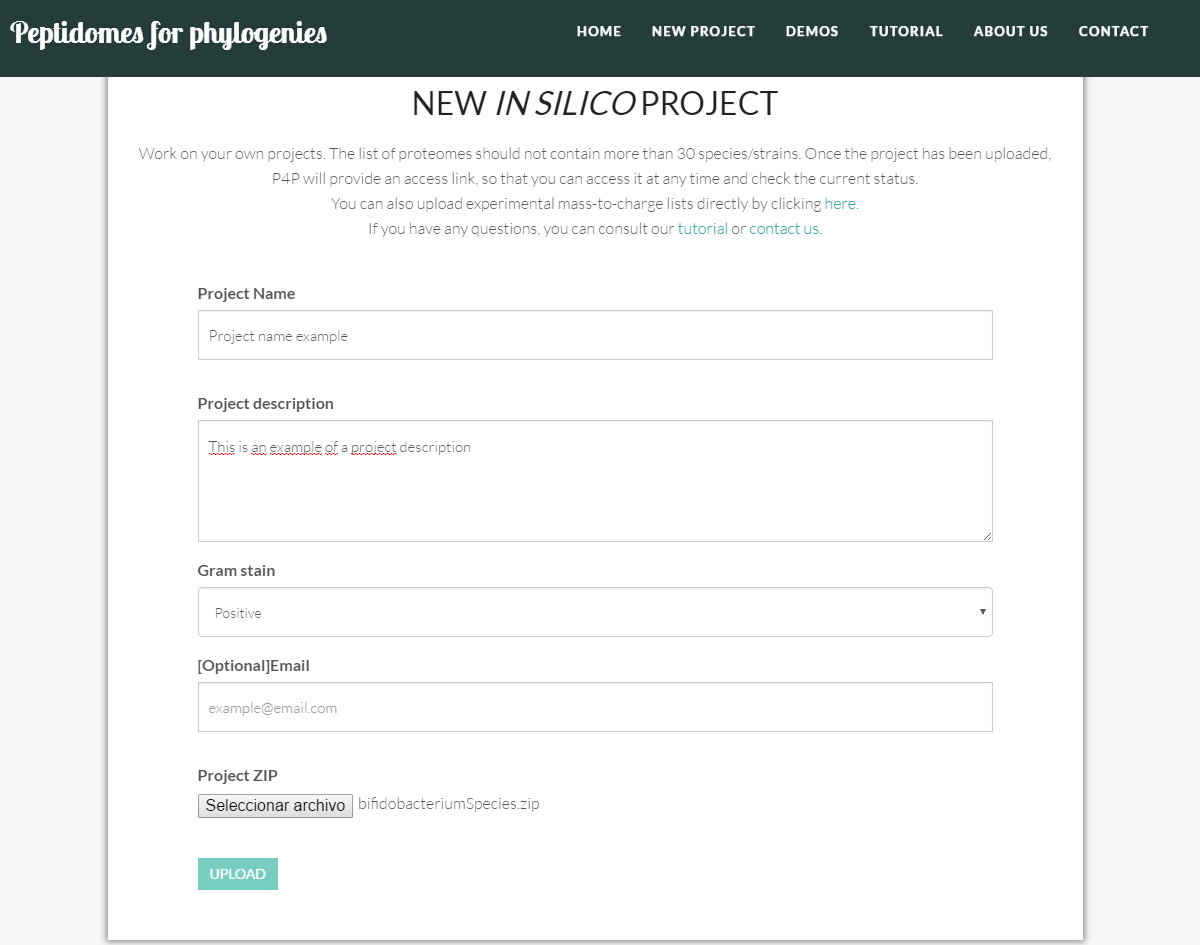
The new project includes the following data:
- Project name: the name of the project. It should be as descriptive as possible and should be between 8 and 80 characters long.
- Project description: a brief description of the scope of the project. Should not exceed 500 characters.
- Gram stain: indicate if the project includes Gram positive or Gram negative type of bacteria.
- Email: [Optional] the email of contact to send the project link and the process updates. This field is optional, because once the project has successfully been uploaded, the tool provides a link (such as http://sing.ei.uvigo.es/p4p/project.php?id=c3bbc604afadc254528e16abacdc0881) for you to monitor the progress of the project at any time.
- Project ZIP: genome files are uploaded as a compressed ZIP file (check an example project ZIP HERE). Make sure that you only include genome files. These genome files must have .faa extension and have an identifying name. Also, for performance reasons, users are not allowed to upload projects containing more than 30 genomes. If you want to analyze a larger project we are happy to enable it offline, please contact us.
New mz/profile project
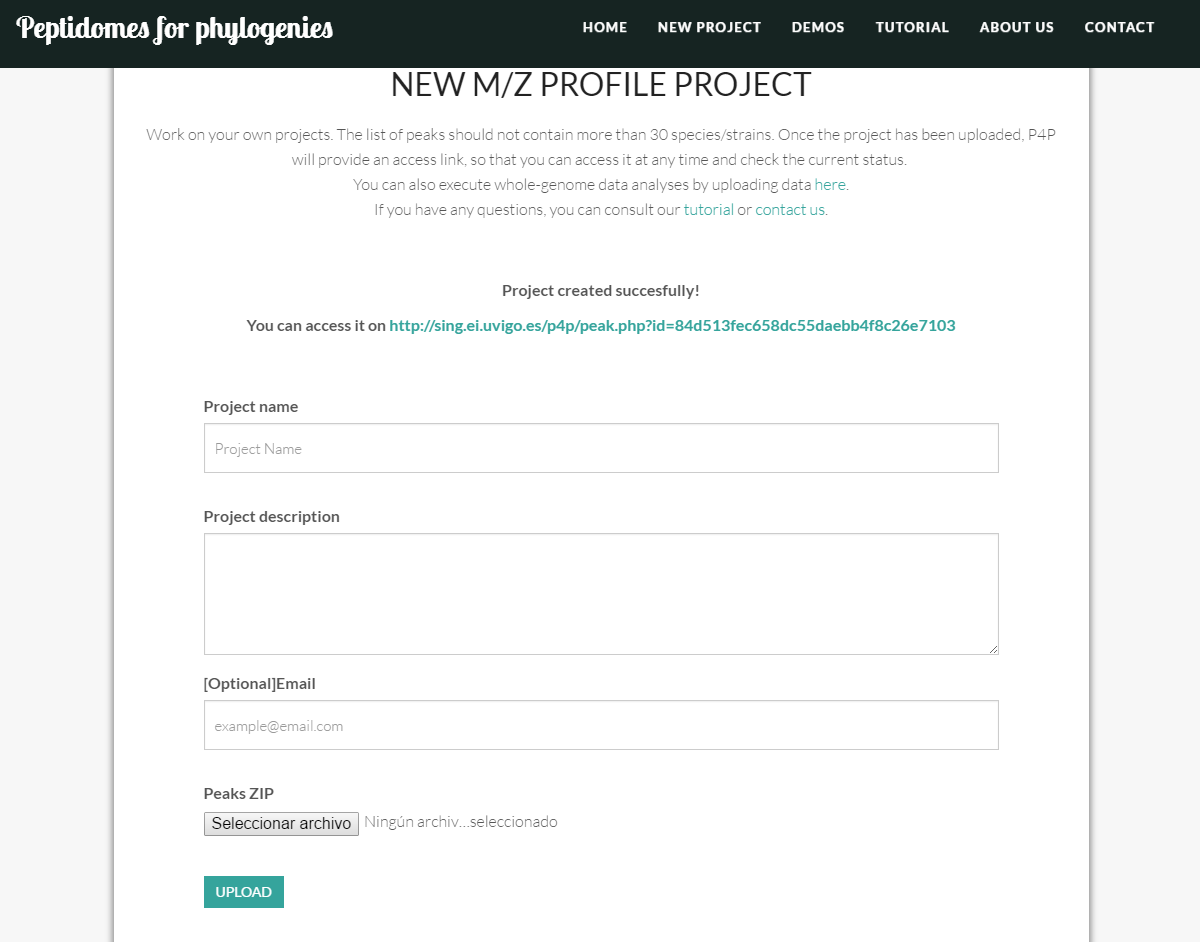
In m/z profile project there are only four fields to fill:

- Project name: the name you want to give the project. It should be as descriptive as possible and should be between 8 and 80 characters long.
- Project description: a brief description of the scope of the project. Should not exceed 500 characters.
- Email: [Optional] the email of contact to send the project link and the process updates. This field is optional, because once the project has successfully been uploaded, the tool provides a link (such as http://sing.ei.uvigo.es/p4p/peak.php?id=8d8e723dc51c5fe7791a45df6d42c4e2) for you to monitor the progress of the project at any time.
- Peaks ZIP: you should upload the peak files as a compressed ZIP file (check an example project ZIP HERE). Make sure that you only include peak files. These peak files must have .peaks extension and have an identifying name. Also, for performance reasons, users are not allowed to upload projects containing more than 30 peaks. If you want to analyze a larger project we are happy to enable it offline, please contact us.
P4P data processing
Once the project has successfully been uploaded, the tool will start to process your project. P4P provides a link (such as http://sing.ei.uvigo.es/p4p/project.php?id=c3bbc604afadc254528e16abacdc0881) for you to monitor the progress of the project at any time (same for peak analysis).
Additionally, if you introduced an email on the form, we will send you this link and process updates (for example, once the project is uploaded and ready to generate, or whenever a NEXUS file / phylogenetic tree is generated).
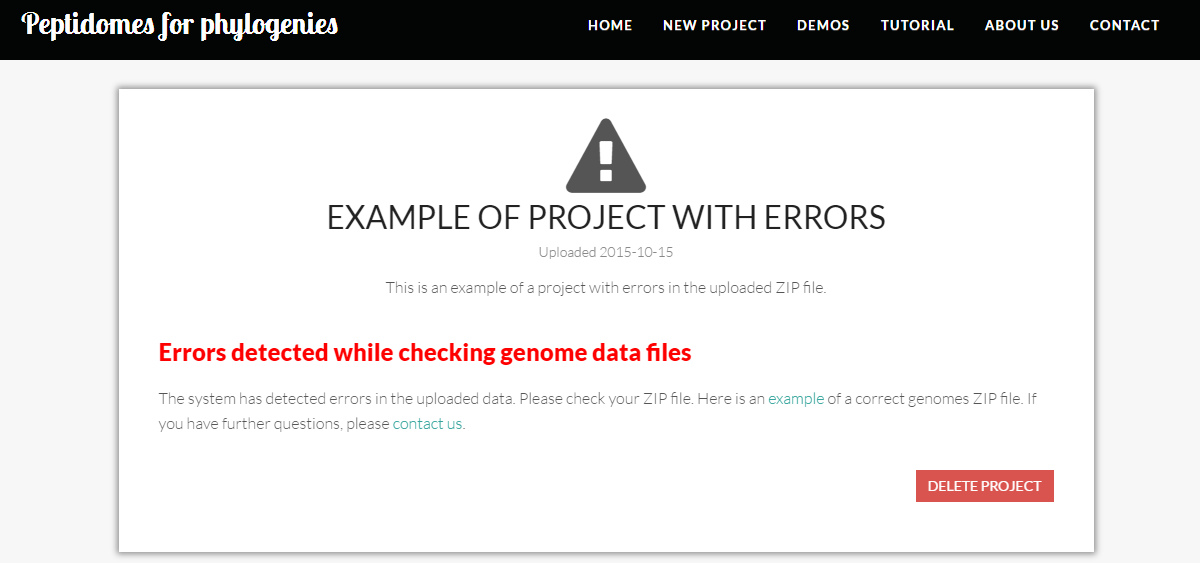
If an error occurs during ZIP file upload, P4P will prompt an error message, as shown in the following project.
Inside an in silico project
Project description includes four contents sections:
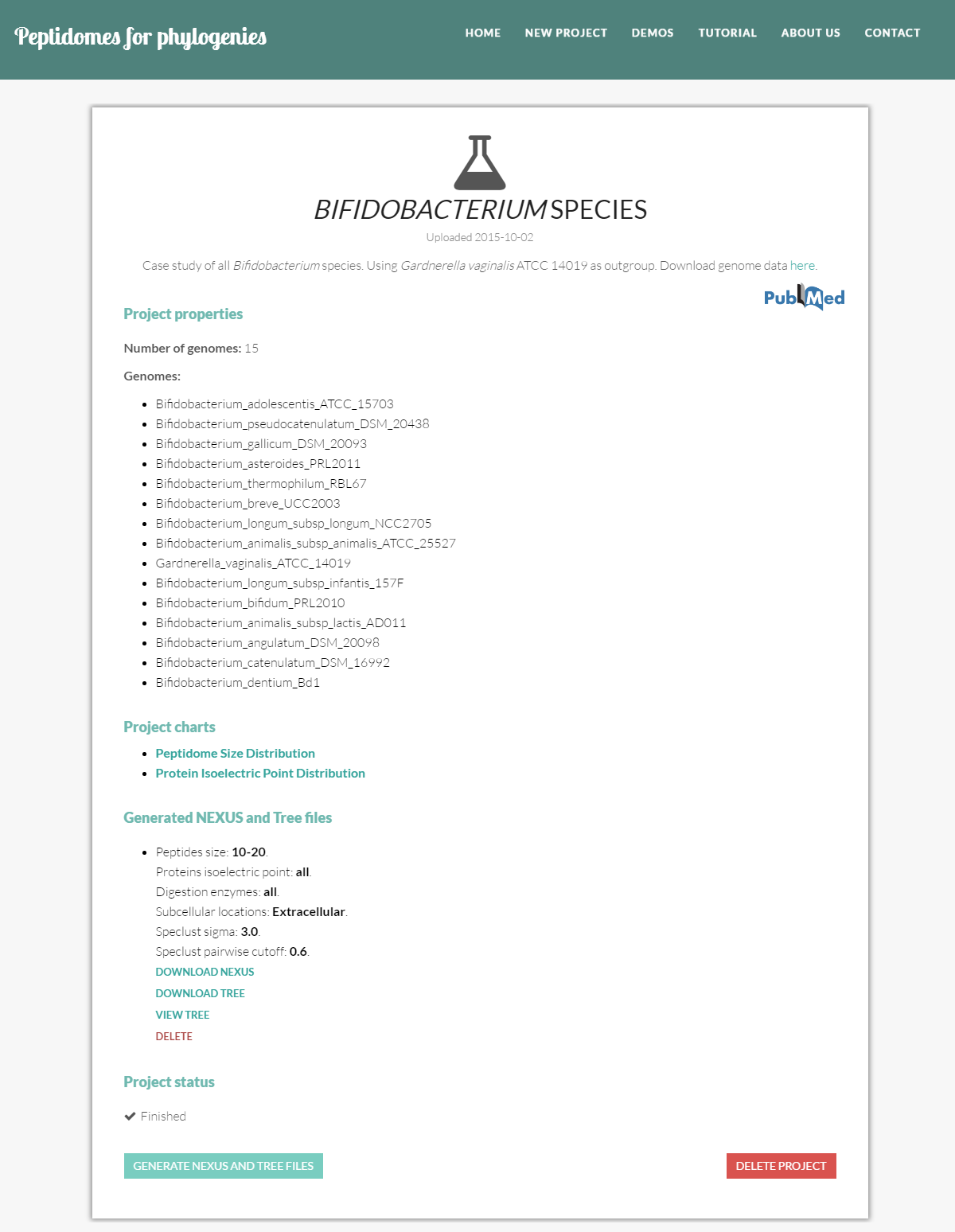
- Project properties: information about the genomes in the project. Namely, the number of genomes and the name of each genome file. During the upload process, this information will be continuously updated; the list will be final once P4P begins processing the project, i.e. the state of the project changes to "Digesting proteins".
- Project charts: here, you can explore the peptidome distribution charts.
- Generated NEXUS and Tree files: all NEXUS and tree files generated for this project.
- Project status: the current state of execution of the project. (see project status section)
Besides looking into the above described information you can perform two actions:
- Generate NEXUS and tree file: to trigger the generation of new NEXUS data files.
- Delete project: to eliminate the project and all its contents.
You can explore the operation of a P4P in silico project in this demo.
In silico project status
During the life cycle of a project, it will undergo four possible states:
- Uploading genomes: this state indicates that P4P is still uploading the content of the genome files. In this state, you are not allowed to explore the peptidome distribution charts, generate NEXUS and tree files or delete the project. Once this process ends, the project status will be changed to "Digesting proteins".
- Digesting proteins: the tool is digesting the proteins of all genomes. At this point, you are not allowed to explore the peptidome distribution charts, generate NEXUS and tree files or delete the project. Once this process ends, the project status will change to "Finished".
- Generating NEXUS and tree file: at this point P4P is generating a NEXUS file for the project. You are not allowed to request the generation of new NEXUS and tree files or delete the project until this process finishes, and project status switches back to "Finished", but you has access to the NEXUS and tree files as well as to the graphs.
- Finished: this state indicates that all processing is terminated and P4P is ready to generate new NEXUS and tree files. At this point, you has access to the NEXUS and tree files as well as to the graphs.
Peptidome distribution
P4P enables the inspection of peptidome distribution charts as means to help you select the most interesting peptides to be included in the NEXUS file. Specifically you may explore:
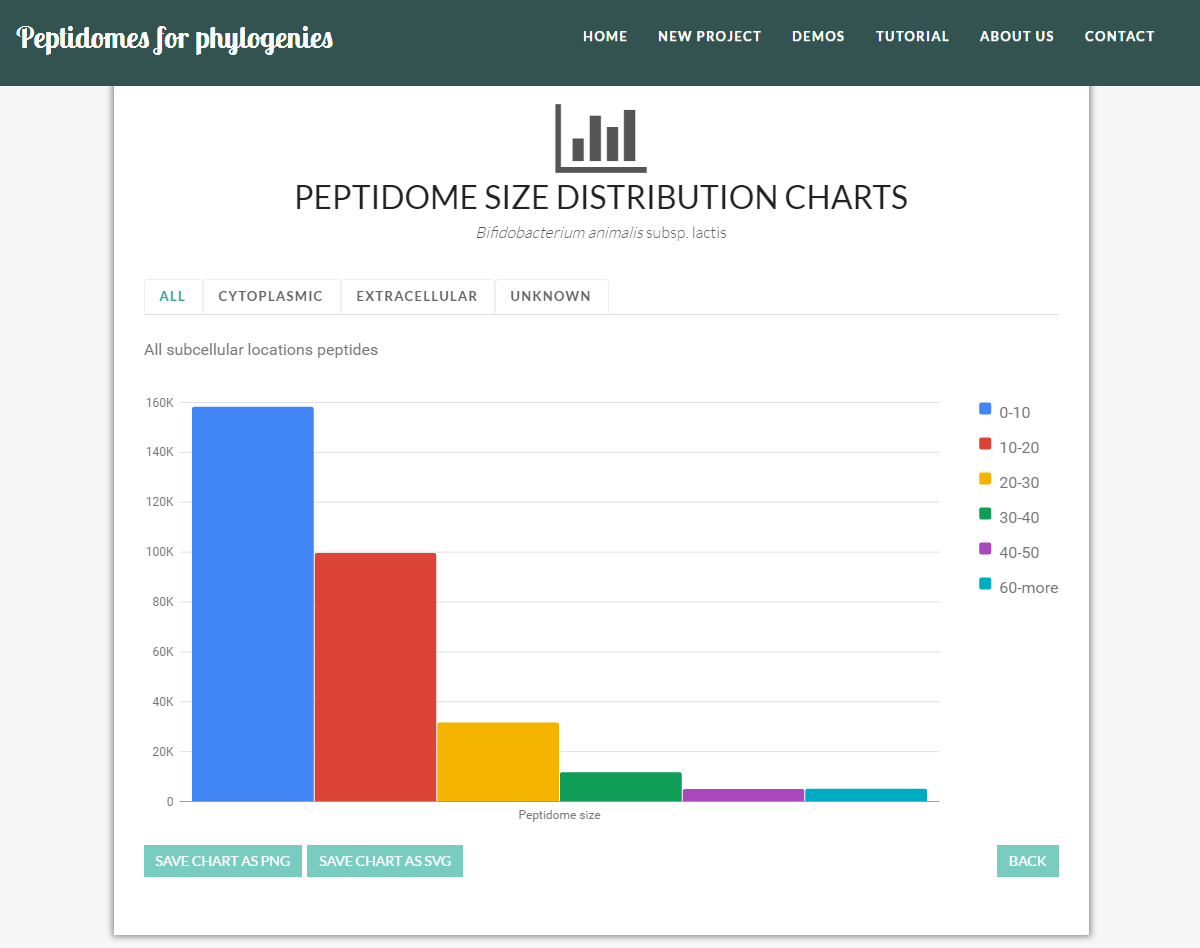
- Peptidome size distribution: i.e. the distribution of the peptides by peptide size EXAMPLE.
- Isoelectric point distribution: i.e. the distribution of peptides by the isoelectric point EXAMPLE.
You may also explore peptidome distribution by subcellular localization, notably look into "all peptides", "cytoplasmic peptides", "extracellular peptides", and "peptides with unknown subcellular location" (as shown in the figure above).
Generating NEXUS and tree files
NEXUS and tree files are the main outputs of P4P analysis. You may generate them once the project is at on hold status.
Simply, click on the "Generate nexus/tree files" button at the project’s page, and fill in desired specifications.
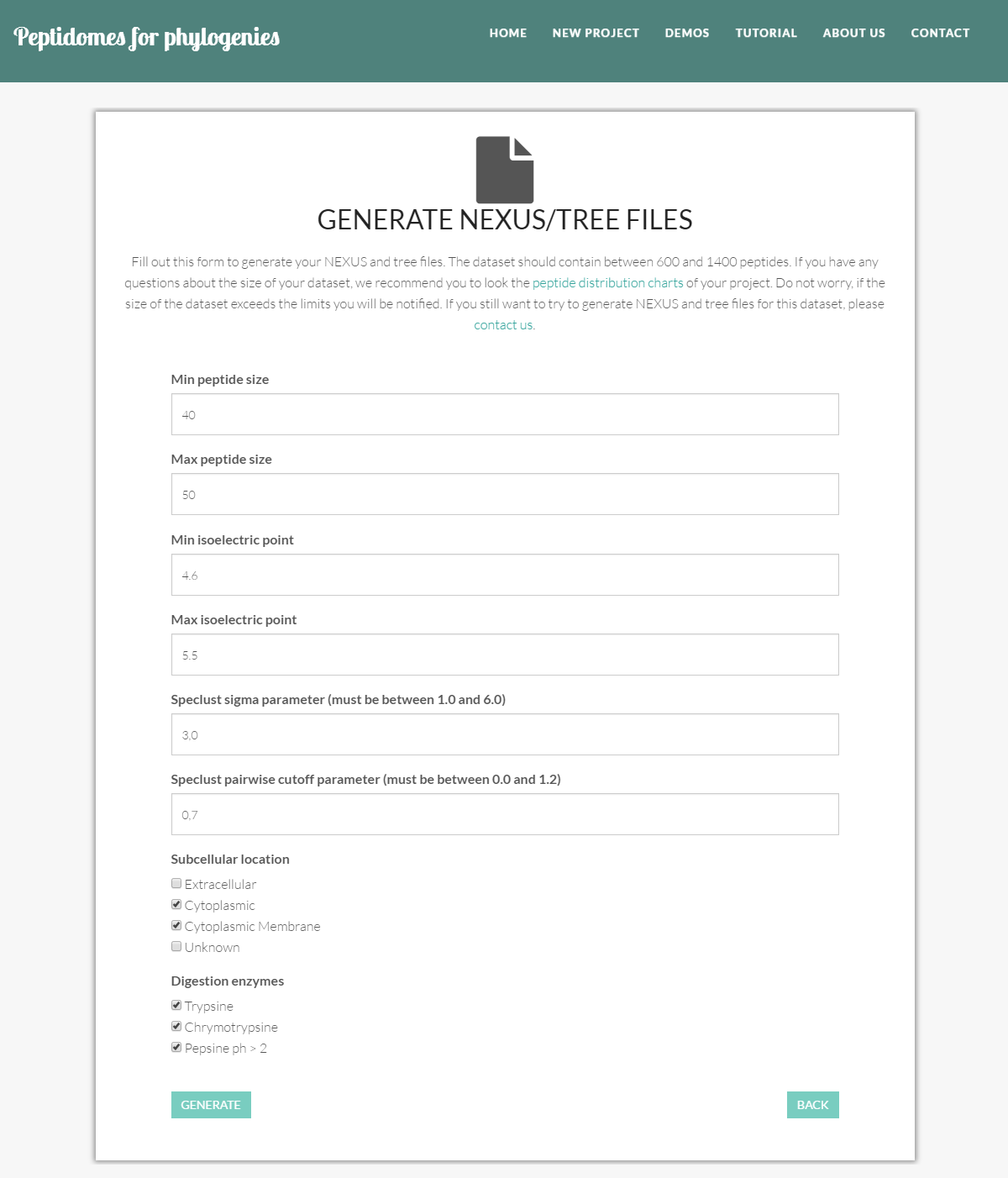
- Min peptide size: the minimum size of the peptides (the minimum number of amino acids) to be selected.
- Max peptide size: the maximum size of the peptides (the maximum number of amino acids) to be selected.
- Min isoelectric point: the lowest isoelectric point of the proteins to be considered.
- Max isoelectric point: the highest isoelectric point of the proteins to be considered.
- Speclust sigma parameter: This is a parameter for running Speclust. This parameter specifies the measurement uncertainty in mass; to use when matching two peaks from different peak lists. This value must be between 1.0 and 6.0.
- Speclust pairwise cutoff parameter: This is a parameter for running Speclust. This parameter is used when all pairs of peak lists are investigated for shared peaks. Peaks are considered pairwise in common if they are matched and the peak match score is larger than the pairwise cut-off. For each pair of peak lists, peaks that are pairwise in common are printed. This value must be between 0.0 and 1.2.
- Subcellular location: the subcellular location of the selected peptides, i.e. cytoplasmic peptides, cytoplasmic membrane peptides, extracellular peptides, and peptides with unknown subcellular location. You must select one or more locations.
- Digestion enzymes: the enzymes used to digest the proteins and produce the peptides. Options are trypsin, chymotrypsin and pepsine ph > 2. You may select one or more multiple digestion enzymes.
When submitting the specifications, you will be shown the commands with their respective parameters to confirm the execution.
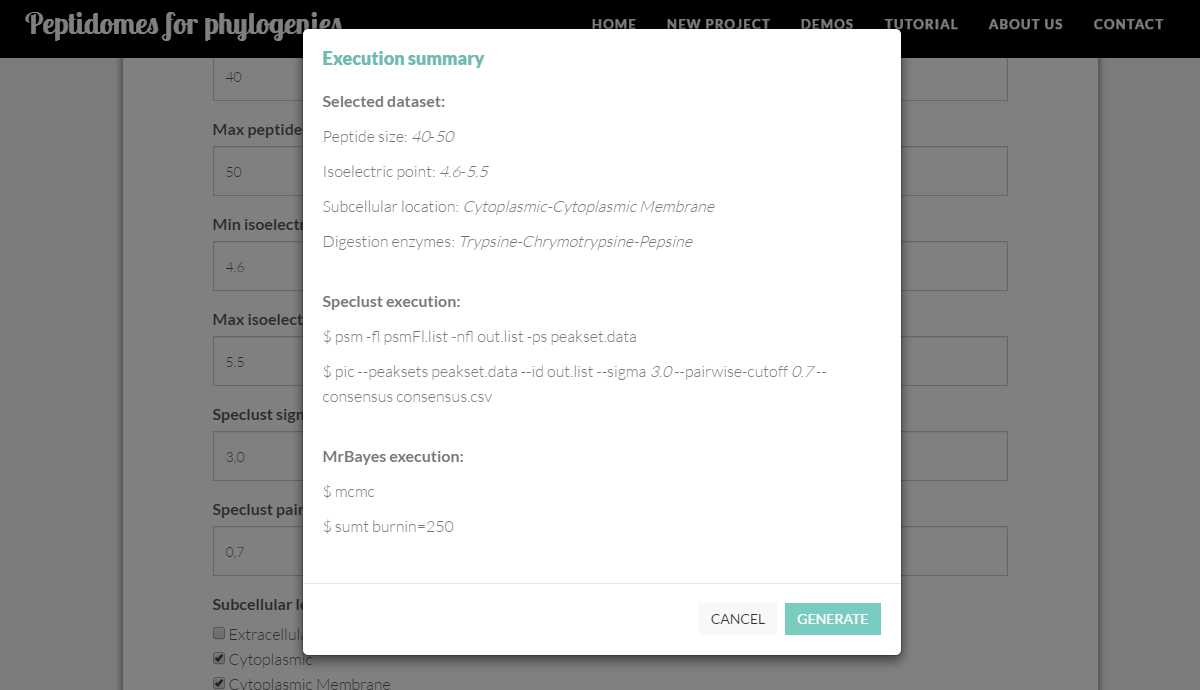
Before executing and calculating NEXUS files and phylogenetic trees, P4P will query our database to check the size of the dataset. This query can be extended by a couple of minutes. A circular animation will be displayed during this time.
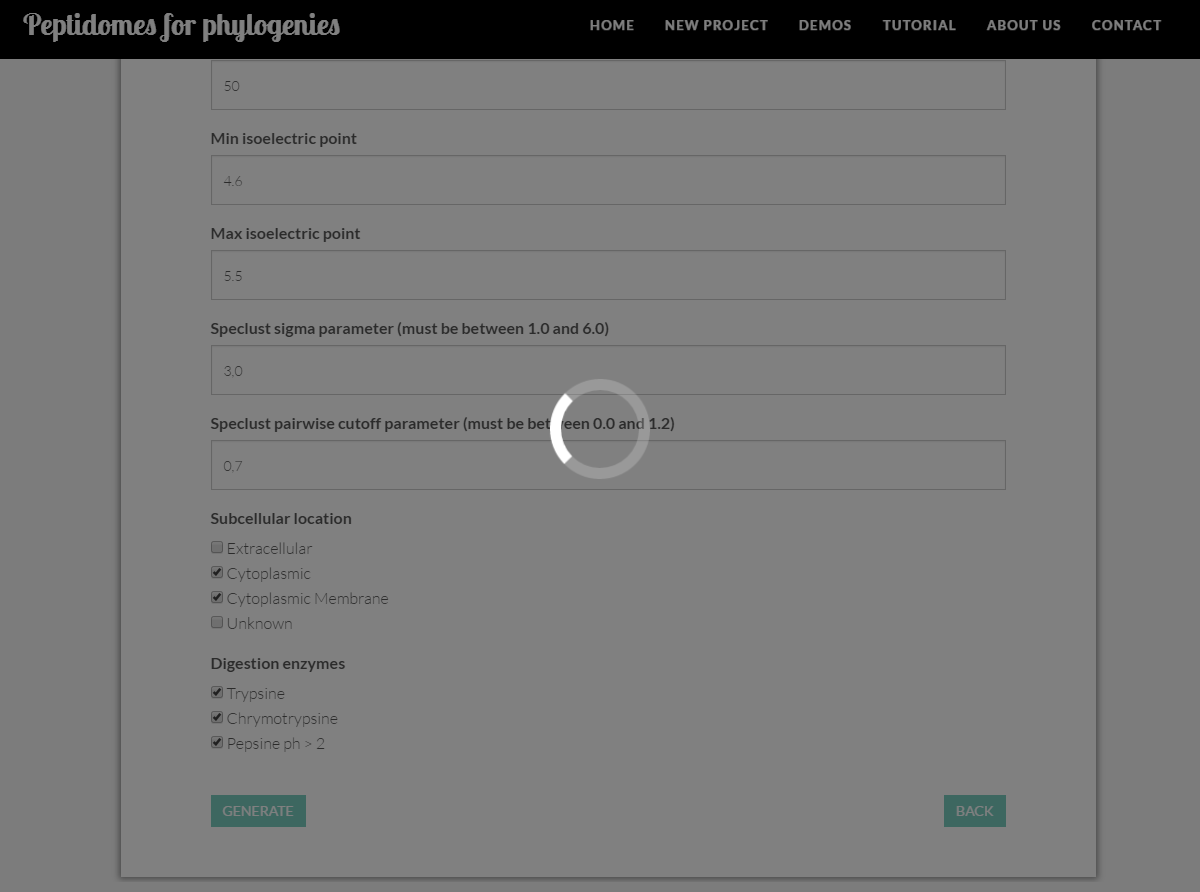
For efficiency reasons, the tool will only generate files containing between 600 and 1400 peptides. You may estimate dataset size by looking into the peptidome distribution charts (see peptidome distribution section).
Inside a m/z profile project
Project description includes four contents sections:

- Project properties: information about the experimental samples in this project. Namely, the number of samples and the name of each peak file. During the upload process, this information will be continuously updated; the list will be final once P4P begins generating the NEXUS and tree file, i.e. the state of the project changes to "Generating NEXUS and tree file".
- Generated NEXUS and tree files: all NEXUS and tree files generated for this project.
- Project status: the current state of execution of the project (see project status section).
Besides looking into the above described information you can perform two actions:
- Delete project: to eliminate the project and all its contents.
You can explore the operation of a P4P m/z profile project in this demo.
If P4P finds an error in the ZIP file during the uploading, no information will be displayed except for an error message, as shown in the following project.
M/z profile project status
During the life cycle of a project, it will undergo four possible states:
- Uploading peaks: this state indicates that P4P is still uploading the content of the peaks files. When this process finish the project status switches back to "Generating NEXUS and tree file".
- Generating NEXUS and tree file: this state indicates that P4P is generating the NEXUS and tree file for the project. When this process finish the project status switches back to "Finished".
- Finished: this state indicates that the project has been finished generate NEXUS and tree file.
Visualizing your trees
P4P allows the visualization of the generated trees, including the following operations:
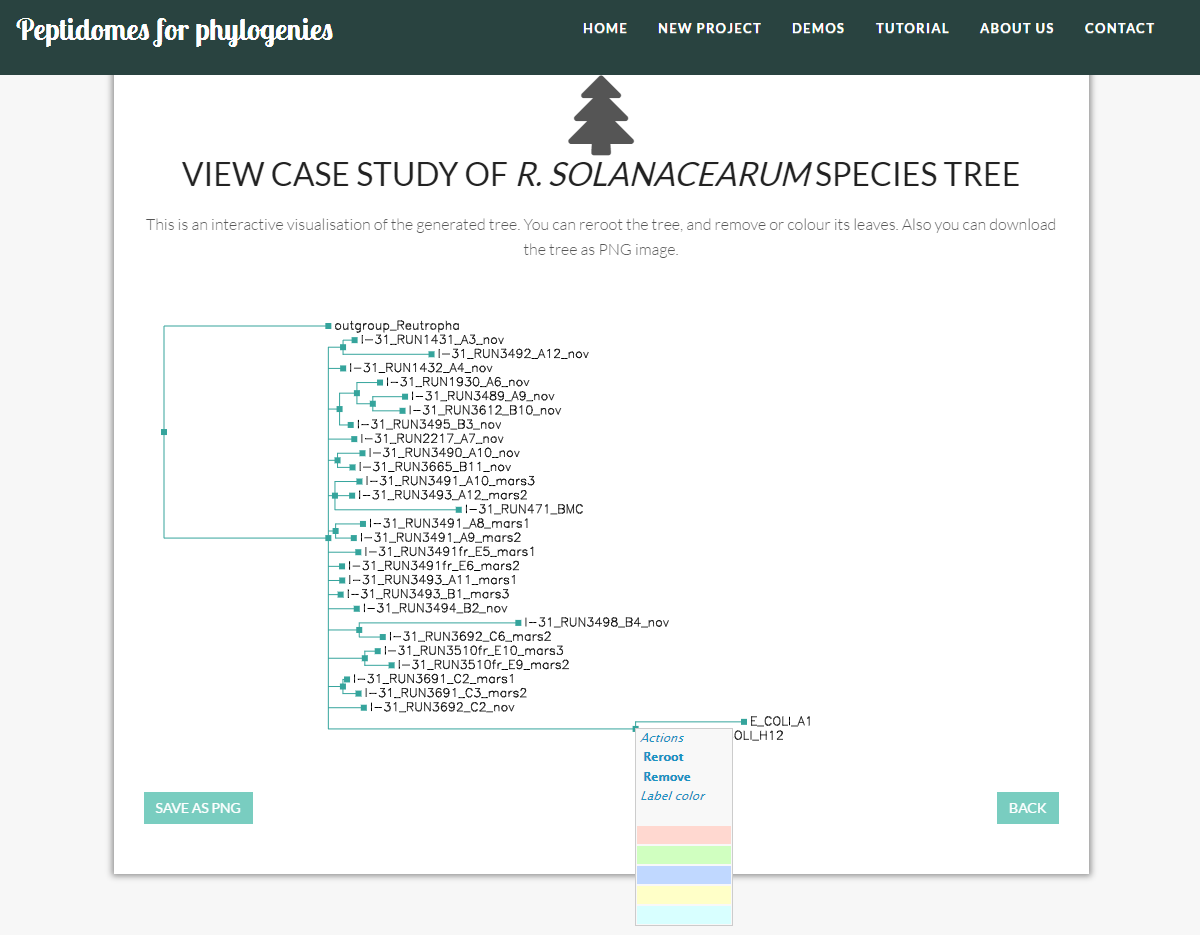
- Reroot the tree: i.e. to change an outgroup.
- Delete leaves: e.g. to improve the visualization of certain parts of the tree.
- Coloring leaves. e.g. to highlight clusters or "loose" branches.
These options are available by clicking on the green square of each of the tree leaves.
You can explore the operation of the P4P visualization tool here.