Main Page
From PileLine
Contents |
What's new
PileLine 1.1 has been released on Feb 11, 2011
The major changes in this version are:
- New pileline-fulljoin command to join n GP files.
- New pileline-nsmc mode: intervals mode. Now it can check the reproducibility of mutations by entire intervals (i.e.:genes, provided as .bed), instead of only exact genome position.
- Added BGZF compatibility. This is the samtools compressed format of GP files. All PileLine commands are adapted to receive both bgz-compressed or uncompressed files, transparently. If you want to know how to compress your GP files, please see: Compress/index input with bgzip+tabix
- Added .fai compatibility for genome indexes (needed in pileline-genotest). The pileline-genindex command is now deprecated. You should use the "samtools faidx" command instead.
- Added more flexibility to include custom GP files, by indicating the sequence, start and stop columns in files.
- Bugfix: Bed files is treated in the standard form: (0-based and the last position in the interval is excluded).
- Bugfix: Prevent fastseek from hanging due to bad input files (i.e.: zip compressed, non-ascii, non tab-separated). A small heuristic check is included before processing the file.
Please note: we are updating the commands help wiki pages
Welcome to PileLine Wiki
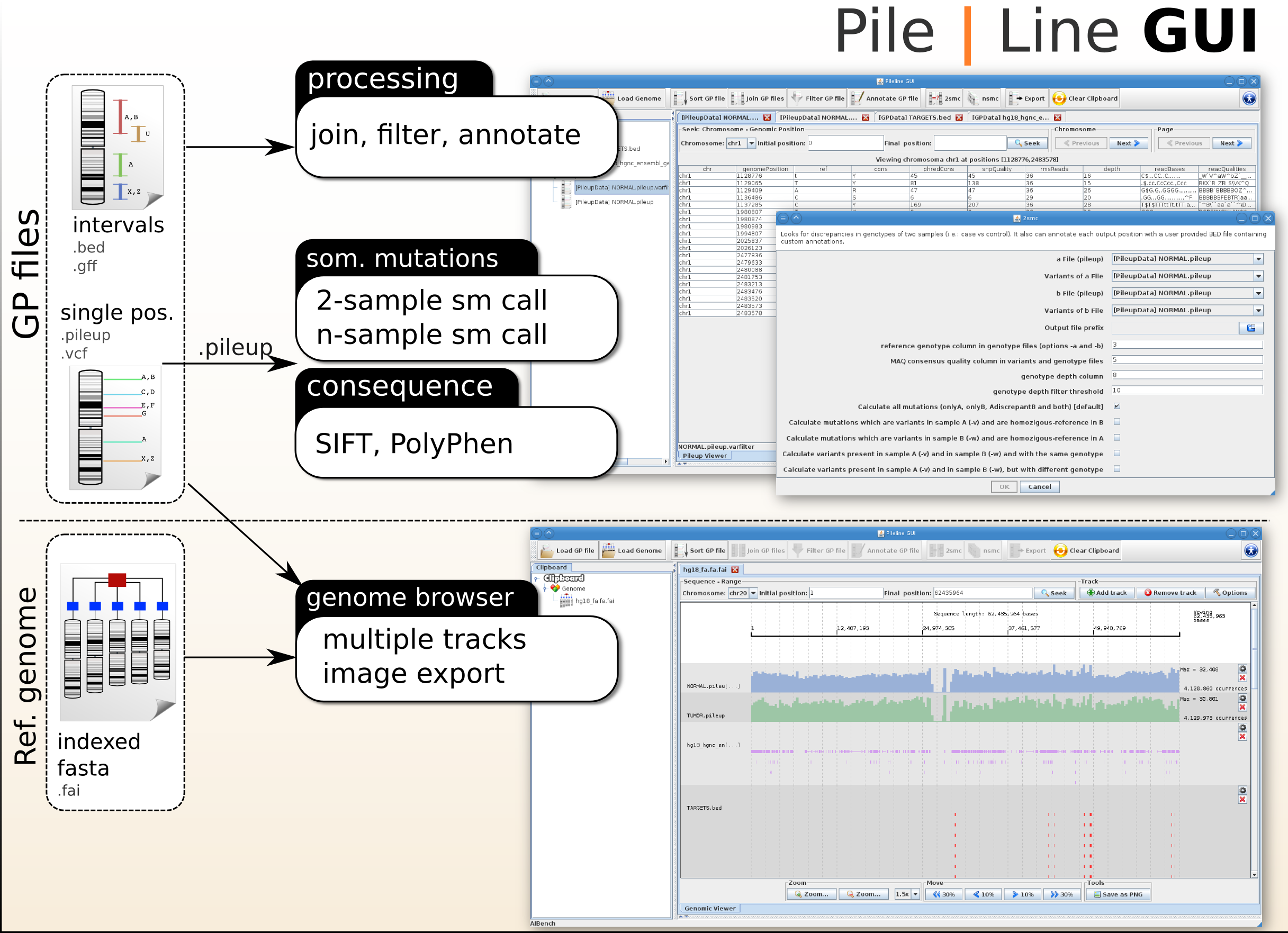
PileLine is a flexible command-line toolkit for efficient handling, filtering, and comparison of genomic position (GP) files produced by next-generation sequencing experiments (i.e. pileup, BED,GFF, or VCF files). PileLine is designed to be memory efficient by performing on-disk operations over sorted GP files directly.
PileLine is available for downloading at: http://sourceforge.net/projects/pilelinetools/
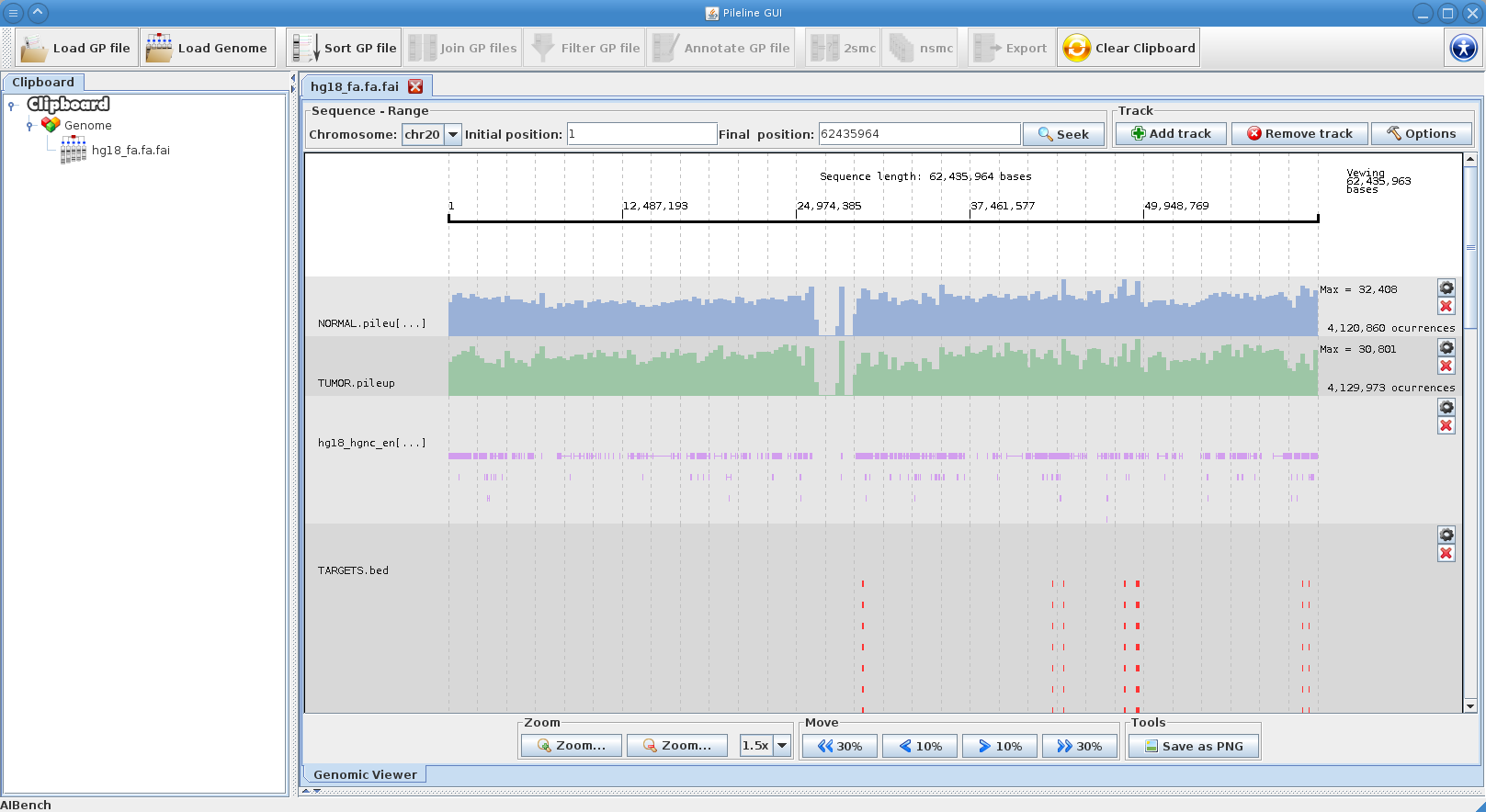
PileLine GUI is under development and includes a front-end of the PileLine toolkit, plus a genome browser.
Main Features
- Quick filtering and search within GP files without indexing steps.
- GP files comparisons.
- Full annotation of GP files with human dbSNP, HGNC Gene Symbol and Ensembl IDs. Custom annotations are also allowed and may be supplied through standard .BED or .GFF files.
- SIFT, PolyPhen-2 and Firestar compatible inputs to facilitate the biological interpretation of huge lists of variants.
- Genotyping quality control functionality to estimate performance metrics (Harismendi et al. 2009) on detecting homo/heterozigote variants against a given gold standard genotype.
- Modular design to facilitate the inclusion of new functionalities.
Getting started
New to PileLine? Please, follow our Quick Start.
PileLine Commands
Processing and Annotation Commands
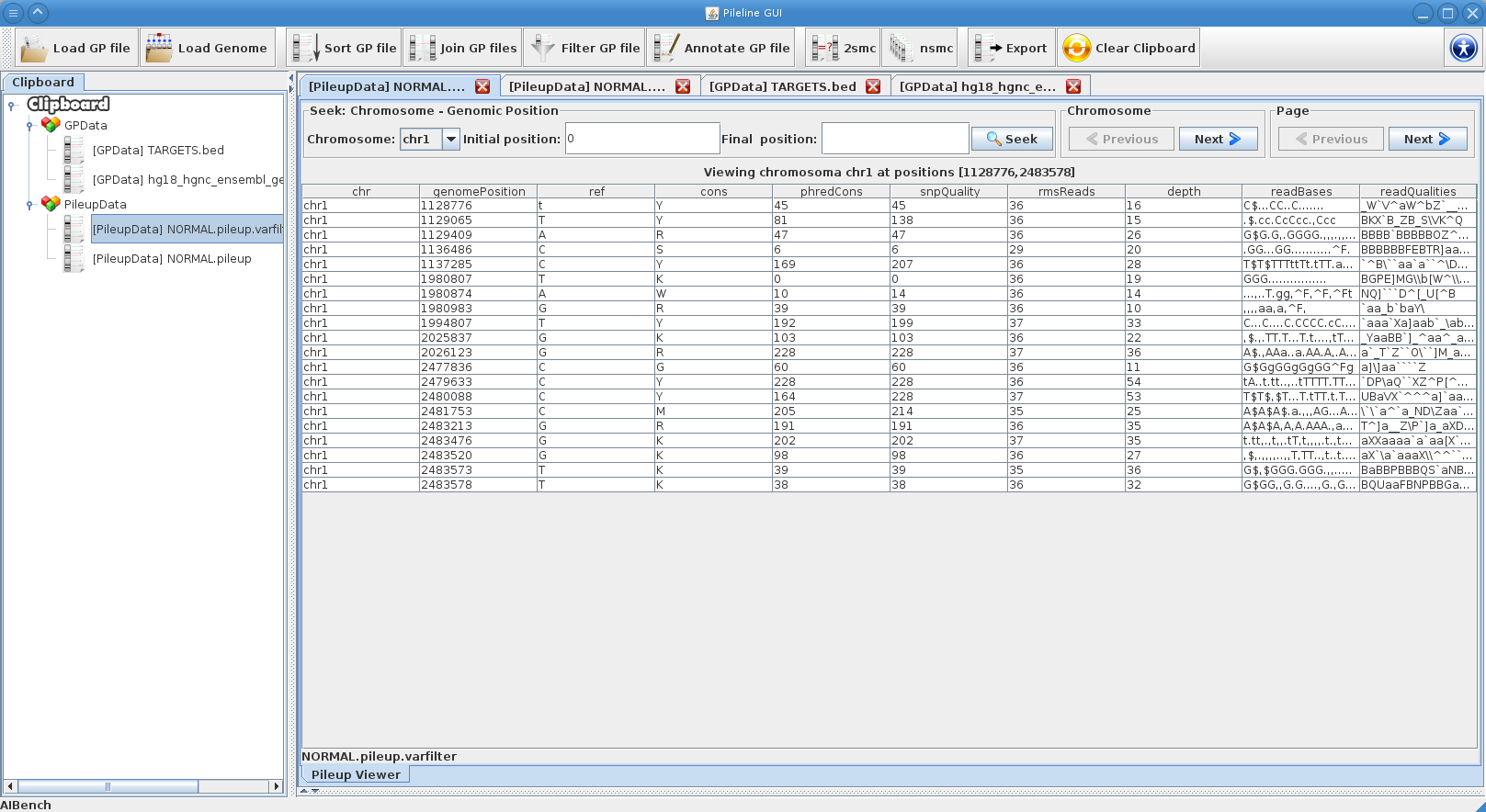
- pileline-fastseek
Prints a given range of a GP file.
- pileline-sort
Sorts GP files by coordinate.
- pileline-fastjoin
Joins two SORTED GP files.
- pileline-rfilter
Filters (or annotates) a positional file with range-based annotations (in bed format). Each position that is inside of a specific range is annotated.
- pileline-pileup2sift
Generates SIFT compatible infiles from pileup files.
- pileline-pileup2polyphen
Generates PolyPhen-2 compatible infiles from pileup files.
- pileline-pileup2firestar
Generates Firestar compatible infiles from GP files.
Analysis Commands
- pileline-2smc
Looks for discrepancies in genotypes of two samples (i.e.: case vs control). It also can annotate each output position with a user provided BED file containing custom annotations.
- pileline-nsmc
Compares n samples reporting consistent variants.
- pileline-genotest
Calculates the NGS performance on genotyping, surveying a set of genomic positions whose genotype is known in the sample. This functionality requires a previous step using *pileline-genindex command for genome indexing.
Use Cases

- Perform 2 samples comparison
pileline-2smc.sh –a <file_A.pileup> –b <file_B.pileup> –v <variants_file_A.pileup> –w <variants_file_B.pileup> –o <out.txt> -d <min_depth>
- Perform n samples comparison
pileline-nsmc.sh --a-samples<GPfile_a1>,<GPfile_a2>,<GPfile_a3> --b-samples <GPfile_b1>,<GPfile_b2>,<GPfile_b3>
- Sort GP files
pileline-sort.sh -i <input_GP_file.txt> -o <outfile.sorted.txt>
- Annotate a GP file with dbSNP
pileline-fastjoin.sh -a <GP_file.txt> -b dbSNP130.txt --left-outer-join
- Annotate a GP file with genes
pileline-rfilter.sh --annotate -A <GP_file.txt> -b <genes.bed>
- Filter pileup to exon loci
pileline-rfilter.sh -A <GP_file.txt> -b <exons.bed>
- Generate column compatible to SIFT intput
pileline-pileup2sift.sh -i <file.pileup>
- Perform a genotyping test for quality control
# Warning: Check that your alleles in the <gold_genotype.sorted> file are expressed in the same strand as the # reference genome sequence used in your NGS experiment. Typically forward (+) strand. ## Step1. #Create reference index <ref_genome.pileline> using pileline-genindex command. pileline-genindex --index -i <ref_genome.pileline> -g <ref_genome.fa> ## Step2. #Create genotest file (required). pileline-genotest --create-genotest-file <experiment.genotest> -p <GP_file.txt> -g <gold_genotype.sorted> -r <ref_genome.pileline> ## Step3. QC analysis. #Generate all performance metrics for several thresholds pileline-genotest -a <experiment.genotest> --batch-t 0,255,1 #Generate values for ROC curve plot (outfile compatible to ROCR R package) pileline-genotest -a <experiment.genotest> --roc #Generate a metrics table of performance at a given threshold. pileline-genotest -a <experiment.genotest> -t <snpq_treshold>
PileLine GUI
PileLine GUI is a front-end of the PileLine toolkit, plus a genome browser. With this intuitive graphical desktop application you can run the following tasks:
- Processing commands of GP files, like seek, join, annotate and filtering.
- Perform 2-samples and n-samples point somatic mutation calling (via the PileLine 2smc and nsmc commands).
- Browse GP files in a interactive local genome browser.
You can download PileLine GUI from Downloads.