Main Page
From PileLine
(→PileLine GUI) |
(→PileLine GUI) |
||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
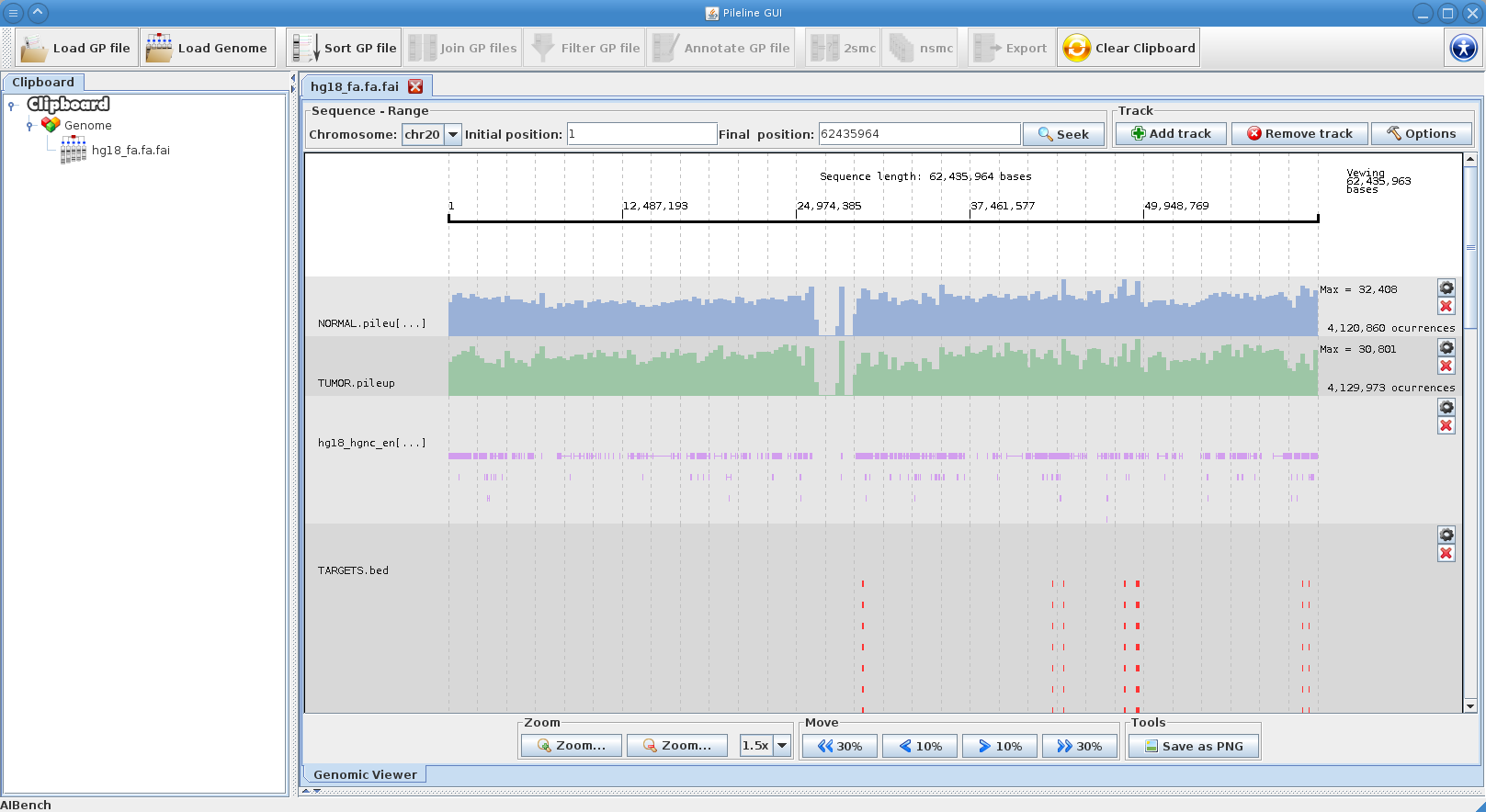
|[[File:genome_browser.png|thumb|PileLine GUI's interactive genome browser.]] | |[[File:genome_browser.png|thumb|PileLine GUI's interactive genome browser.]] | ||
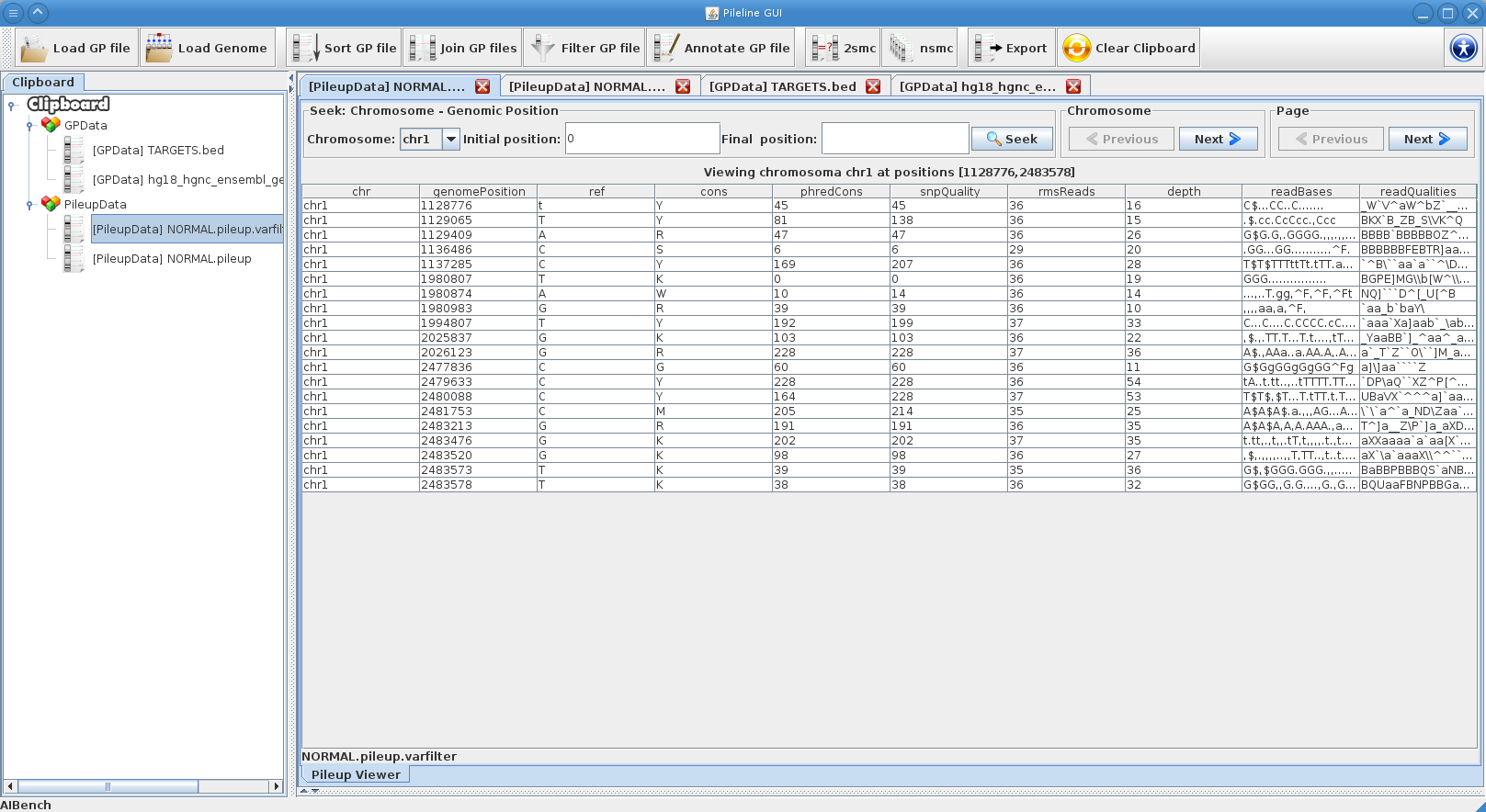
|[[File:gpfiles_view.png|thumb|PileLine GUI showing a instantly-navigable .pileup file.]] | |[[File:gpfiles_view.png|thumb|PileLine GUI showing a instantly-navigable .pileup file.]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can get sample files to test PileLine GUI in our [[Sample_Data|Sample data]]. The following table shows which files are required for which functionality: | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="2" | ||
| + | |-align="left" | ||
| + | !scope="col"| Functionality | ||
| + | !scope="col"| Files | ||
| + | !scope="col"| Description | ||
| + | |-align="left" | ||
| + | !scope="row"| Somatic mutation calling | ||
| + | |||
| + | (2-smc and n-smc) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Media:Control1Files.zip|Control1Files.zip]] (36MB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Media:Case1Files.zip|Case1Files.zip]] (36MB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Media:Control2Files.zip|Control2Files.zip]] (38MB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Media:Case2Files.zip|Case2Files.zip]] (38MB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | | For 2-smc you need at least Control1 and Case1 files. For n-smc, you need all. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''NOTE: This files have only information for the chromosome 10''' | ||
| + | |-align="left" | ||
| + | !scope="row"| Filter and annotation | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | [[Media:DbSNP_36.3.txt.zip|DbSNP_36.3.txt.zip]] (237MB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Media:Hg18_hgnc_ensembl_genes.bed.zip|Hg18_hgnc_ensembl_genes.bed.zip]] (365KB) | ||
| + | | You need at least the genome file. In order to add tracks, you need GP files. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |-align="left" | ||
| + | !scope="row"| Genome Browser | ||
| + | | [http://sing.ei.uvigo.es/pileline/data/hg18.tar.gz hg18.tar.gz] (892MB) | ||
| + | | You need at least the genome file. In order to add tracks, you need GP files. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:26, 4 January 2011
Contents |
Welcome to PileLine Wiki
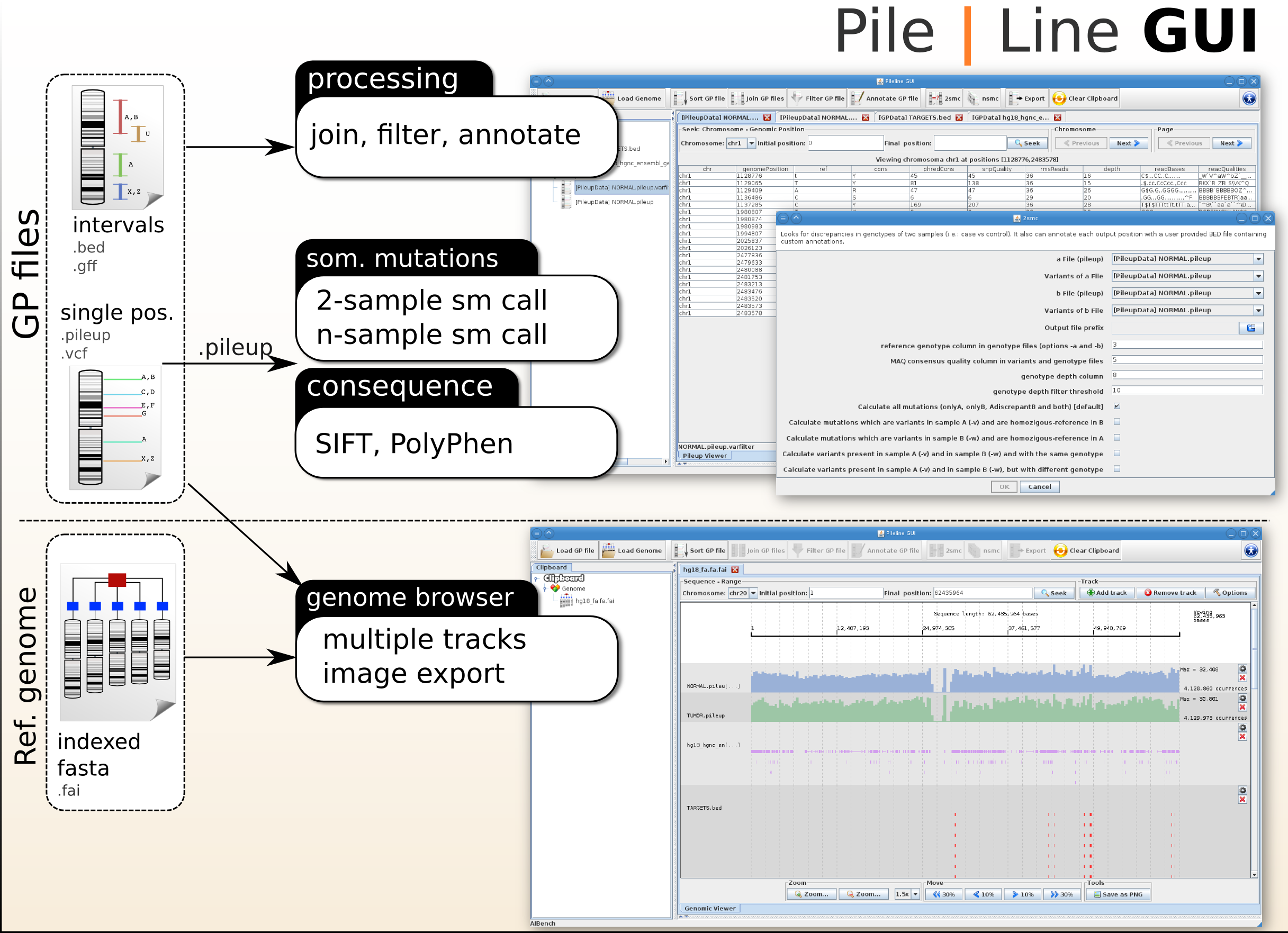
PileLine is a flexible command-line toolkit for efficient handling, filtering, and comparison of genomic position (GP) files produced by next-generation sequencing experiments (i.e. pileup, BED,GFF, or VCF files). PileLine is designed to be memory efficient by performing on-disk operations over sorted GP files directly.
PileLine is available for downloading at: http://sourceforge.net/projects/pilelinetools/
PileLine GUI is a front-end of the PileLine toolkit, plus a genome browser.
Main Features
- Quick filtering and search within GP files without indexing steps.
- GP files comparisons.
- Full annotation of GP files with human dbSNP, HGNC Gene Symbol and Ensembl IDs. Custom annotations are also allowed and may be supplied through standard .BED or .GFF files.
- SIFT, PolyPhen-2 and Firestar compatible inputs to facilitate the biological interpretation of huge lists of variants.
- Genotyping quality control functionality to estimate performance metrics (Harismendi et al. 2009) on detecting homo/heterozigote variants against a given gold standard genotype.
- Modular design to facilitate the inclusion of new functionalities.
Getting started
New to PileLine? Please, follow our Quick Start.
PileLine Commands
Processing and Annotation Commands
- pileline-fastseek
Prints a given range of a GP file.
- pileline-sort
Sorts GP files by coordinate.
- pileline-fastjoin
Joins two SORTED GP files.
- pileline-rfilter
Filters (or annotates) a positional file with range-based annotations (in bed format). Each position that is inside of a specific range is annotated.
- pileline-pileup2sift
Generates SIFT compatible infiles from pileup files.
- pileline-pileup2polyphen
Generates PolyPhen-2 compatible infiles from pileup files.
- pileline-pileup2firestar
Generates Firestar compatible infiles from GP files.
Analysis Commands
- pileline-2smc
Looks for discrepancies in genotypes of two samples (i.e.: case vs control). It also can annotate each output position with a user provided BED file containing custom annotations.
- pileline-nsmc
Compares n samples reporting consistent variants.
- pileline-genotest
Calculates the NGS performance on genotyping, surveying a set of genomic positions whose genotype is known in the sample. This functionality requires a previous step using *pileline-genindex command for genome indexing.
Use Cases

- Perform 2 samples comparison
pileline-2smc.sh –a <file_A.pileup> –b <file_B.pileup> –v <variants_file_A.pileup> –w <variants_file_B.pileup> –o <out.txt> -d <min_depth>
- Perform n samples comparison
pileline-nsmc.sh --a-samples<GPfile_a1>,<GPfile_a2>,<GPfile_a3> --b-samples <GPfile_b1>,<GPfile_b2>,<GPfile_b3>
- Sort GP files
pileline-sort.sh -i <input_GP_file.txt> -o <outfile.sorted.txt>
- Annotate a GP file with dbSNP
pileline-fastjoin.sh –a <GP_file.txt> -b dbSNP130.txt --left-outer-join
- Annotate a GP file with genes
pileline-rfilter.sh --annotate –A <GP_file.txt> –b <genes.bed>
- Filter pileup to exon loci
pileline-rfilter.sh –A <GP_file.txt> –b <exons.bed>
- Generate column compatible to SIFT intput
pileline-pileup2sift.sh -i <file.pileup>
- Perform a genotyping test for quality control
# Warning: Check that your alleles in the <gold_genotype.sorted> file are expressed in the same strand as the # reference genome sequence used in your NGS experiment. Typically forward (+) strand. ## Step1. #Create reference index <ref_genome.pileline> using pileline-genindex command. pileline-genindex --index -i <ref_genome.pileline> -g <ref_genome.fa> ## Step2. #Create genotest file (required). pileline-genotest --create-genotest-file <experiment.genotest> –p <GP_file.txt> –g <gold_genotype.sorted> -r <ref_genome.pileline> ## Step3. QC analysis. #Generate all performance metrics for several thresholds pileline-genotest -a <experiment.genotest> --batch-t 0,255,1 #Generate values for ROC curve plot (outfile compatible to ROCR R package) pileline-genotest -a <experiment.genotest> --roc #Generate a metrics table of performance at a given threshold. pileline-genotest -a <experiment.genotest> -t <snpq_treshold>
PileLine GUI
PileLine GUI is a front-end of the PileLine toolkit, plus a genome browser. With this intuitive graphical desktop application you can run the following tasks:
- Processing commands of GP files, like seek, join, annotate and filtering.
- Perform 2-samples and n-samples point somatic mutation calling (via the PileLine 2smc and nsmc commands).
- Browse GP files in a interactive local genome browser.
You can download PileLine GUI from Downloads.
You can get sample files to test PileLine GUI in our Sample data. The following table shows which files are required for which functionality:
| Functionality | Files | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Somatic mutation calling
(2-smc and n-smc) |
Control1Files.zip (36MB) Case1Files.zip (36MB) Control2Files.zip (38MB) Case2Files.zip (38MB) | For 2-smc you need at least Control1 and Case1 files. For n-smc, you need all.
NOTE: This files have only information for the chromosome 10 |
| Filter and annotation |
DbSNP_36.3.txt.zip (237MB) Hg18_hgnc_ensembl_genes.bed.zip (365KB) | You need at least the genome file. In order to add tracks, you need GP files. |
| Genome Browser | hg18.tar.gz (892MB) | You need at least the genome file. In order to add tracks, you need GP files. |