Multiple sequence alignment (MSA)
can be read and written in a variety of standard
formats. However, available software often does not exactly comply with the
standards, so the task of converting a given MSA to another format correctly
supported by a particular analysis program can be very confusing. ALTER aims to
make life easier for users by taking into consideration both programs and
formats.
ALTER implements a straightforward
workflow that easily guides the user through a 4-step wizard in which the
different options are automatically activated when the required information is
available.
Currently, ALTER has been
successfully tested in Internet Explorer 7, Firefox 3, Opera 9.62, Google Crome
3.0.195.38 and Safari 3 working under Windows XP/Vista, Ubuntu Linux 8.04
version and Mac OSX 10.6.
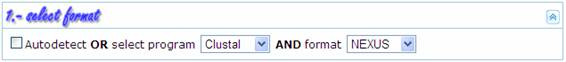
In this step the
user provides information about the format of the MSA to be converted. If  is
selected, ALTER automatically tries to recognize the format of the input MSA;
otherwise the user can specify the required information. The following table
shows the input programs and formats supported at this time by ALTER. This list
will grow in the future according to perceived needs and user suggestions.
is
selected, ALTER automatically tries to recognize the format of the input MSA;
otherwise the user can specify the required information. The following table
shows the input programs and formats supported at this time by ALTER. This list
will grow in the future according to perceived needs and user suggestions.
|
Program
|
Formats
|
|
Clustal
|
ALN,
FASTA, GDE, MSF, NEXUS, PHYLIP, PIR
|
|
MAFFT
|
ALN, FASTA
|
|
TCoffee
|
ALN,
FASTA, MSF, PHYLIP, PIR
|
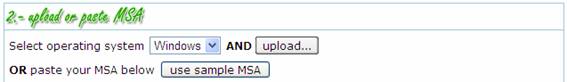
In order to
correctly handle specific issues (i.e., line breaks, carriage returns, etc.)
related to the operating system in which the input sequence file was created, the
user can specify the source OS.
By clicking the  button, a standard input dialog-box is
accessible to select the input MSA file.
button, a standard input dialog-box is
accessible to select the input MSA file.
During file
loading, a progress bar is automatically displayed;
For testing
purposes, we also provide a  button to load sample data in. Once the input
MSA has been processed, its content is showed in read-only mode.
button to load sample data in. Once the input
MSA has been processed, its content is showed in read-only mode.

All the relevant
information related to the process of loading and recognizing the input data is
automatically categorized (info, error, warning) and displayed in a series of
log panels (refer to ALTER log panels section in this document for more
information).
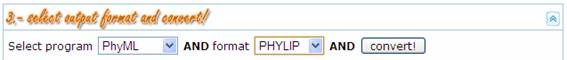
In this step the
user provides information about both the program and the format desired for the
output MSA. The following table shows the input programs and formats currently
supported by ALTER. This list will grow in the future according to perceived
needs and user suggestions.
|
Program
|
Formats
|
|
ANY
|
ALN,
FASTA, GDE, MEGA, MSF, NEXUS, PHYLIP, PIR
|
|
jModelTest
|
ALN,
FASTA, MSF, NEXUS, PHYLIP, PIR
|
|
MrBayes
|
NEXUS
|
|
PAML
|
NEXUS,
PHYLIP
|
|
PAUP
|
MEGA, MSF,
NEXUS, PHYLIP, PIR
|
|
PhyML
|
PHYLIP
|
|
ProtTest
|
NEXUS,
PHYLIP
|
|
RAxML
|
PHYLIP
|
|
TCS
|
NEXUS,
PHYLIP
|
|
CodABC
|
PHYLIP
|
Additionally, there are some options that control
other aspects of the MSA generated. The user can activate/deactivate them in
the  tab of the
tab of the  panel.
panel.
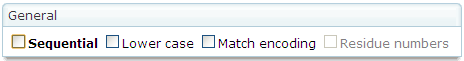
A brief
explanation about each option is given in the following table.
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
|
Lower case
|
Outputs
the sequences using lower case characters.
|
|
Match encoding
|
Uses
match characters (character “.”) to
indicate that the same residue is located in the same position of the first
sequence. This option is not available for MSF format since it prints gaps as
“.” characters.
|
|
Residue numbers
|
Outputs
the sum of the number of residues to that point next to each line of each
sequence. This option is only available for ALN format.
|
|
Sequential
|
Outputs
the sequences in sequential format. This option is only available for NEXUS
and PHYLIP formats.
|
SEQUENCE COLLAPSING
Importantly, ALTER can collapse sequences to
haplotypes (unique sequences) during the conversion among formats. The options
controlling this transformation are available in the  tab of the
tab of the  panel.
panel.
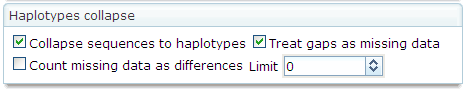
A brief
explanation about each option is given in the following table.
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
|
Collapse sequences to haplotypes
|
This
option enables the haplotype collapse feature. When checked, it activates the
rest of the options to handle this process.
|
|
Treat gaps as missing data
|
Indicates
if gaps should be treated as missing data or not. If this option is not
checked, gaps are treated as a fifth state.
|
|
Count missing data as differences
|
Indicates
if missing data should be counted as differences or not. If this option is
not checked, missing data is treated as any other kind of residue.
|
By pressing the  button ALTER generates the output MSA file for
the specified program and format. All the relevant information related with the
process of converting and/or collapsing the source file is automatically
categorized (info, error, warning) and displayed by ALTER through a series of
log panels (refer to ALTER log panels section in this document for more
information).
button ALTER generates the output MSA file for
the specified program and format. All the relevant information related with the
process of converting and/or collapsing the source file is automatically
categorized (info, error, warning) and displayed by ALTER through a series of
log panels (refer to ALTER log panels section in this document for more
information).
In order to
download the resulting MSA, the user has to specify the target operating system.
By clicking the  button,
a window panel opens offering the user the capability of selecting the download
location.
button,
a window panel opens offering the user the capability of selecting the download
location.
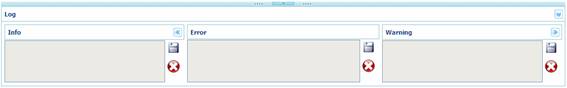
All the information related
with the conversion of MSA files is automatically classified by ALTER using
three main categories: info, error and warning.
Each panel is independent and
it has its own buttons for saving ( )
and deleting (
)
and deleting ( )
the information displayed. Moreover, the left and right panels can be minimized
in order to gain space for the error panel.
)
the information displayed. Moreover, the left and right panels can be minimized
in order to gain space for the error panel.
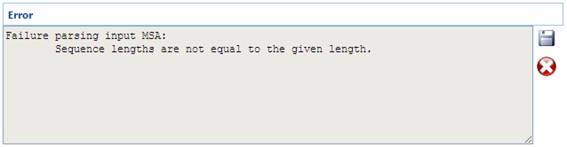
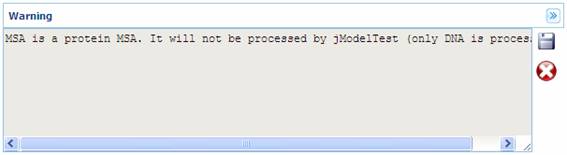
Below, some examples of
different program outputs are showed:

[PROGRAMS]
[input]
[1] Clustal:
http://www.clustal.org/
[2] MAFFT:
http://align.bmr.kyushu-u.ac.jp/mafft/software/
[3] T-Coffee: http://www.tcoffee.org/
[output]
[4] jModelTest:
http://darwin.uvigo.es/software/jmodeltest.html
[5] MrBayes: http://www.mrbayes.net
[6] PAML:
http://abacus.gene.ucl.ac.uk/software/paml.html
[7] PAUP:
http://paup.csit.fsu.edu/
[8] PhyML:
http://www.atgc-montpellier.fr/phyml/
[9] ProtTest:
http://darwin.uvigo.es/software/prottest.html
[10] RAxML:
http://icwww.epfl.ch/~stamatak/index-Dateien/Page443.htm
[11] TCS:
http://darwin.uvigo.es/software/tcs.html
[12] CodABC:
https://code.google.com/p/codabc/
[FORMATS]
[12] The Phylogenetic
Handbook: A Practical Approach to Phylogenetic Analysis and Hypothesis Testing,
2nd Edition. (2009). Philippe Lemey, Marco Salemi and Anne-Mieke Vandamme
(Editors). Cambridge
University Press. ISBN
978-0-521-87710-7.